R-Ras signals through specific integrin alpha cytoplasmic domains to promote migration and invasion of breast epithelial cells
- PMID: 10352023
- PMCID: PMC2133135
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.145.5.1077
R-Ras signals through specific integrin alpha cytoplasmic domains to promote migration and invasion of breast epithelial cells
Abstract
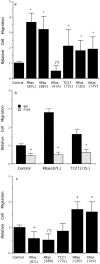
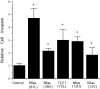
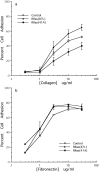
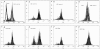
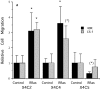
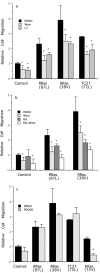
Specificity and modulation of integrin function have important consequences for cellular responses to the extracellular matrix, including differentiation and transformation. The Ras-related GTPase, R-Ras, modulates integrin affinity, but little is known of the signaling pathways and biological functions downstream of R-Ras. Here we show that stable expression of activated R-Ras or the closely related TC21 (R-Ras 2) induced integrin-mediated migration and invasion of breast epithelial cells through collagen and disrupted differentiation into tubule structures, whereas dominant negative R-Ras had opposite effects. These results imply novel roles for R-Ras and TC21 in promoting a transformed phenotype and in the basal migration and polarization of these cells. Importantly, R-Ras induced an increase in cellular adhesion and migration on collagen but not fibronectin, suggesting that R-Ras signals to specific integrins. This was further supported by experiments in which R-Ras enhanced the migration of cells expressing integrin chimeras containing the alpha2, but not the alpha5, cytoplasmic domain. In addition, a transdominant inhibition previously noted only between integrin beta cytoplasmic domains was observed for the alpha2 cytoplasmic domain; alpha2beta1-mediated migration was inhibited by the expression of excess alpha2 but not alpha5 cytoplasmic domain-containing chimeras, suggesting the existence of limiting factors that bind the integrin alpha subunit. Using pharmacological inhibitors, we found that R-Ras induced migration on collagen through a combination of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and protein kinase C, but not MAPK, which is distinct from the other Ras family members, Rac, Cdc42, and N- and K-Ras. Thus, R-Ras communicates with specific integrin alpha cytoplasmic domains through a unique combination of signaling pathways to promote cell migration and invasion.
Figures

References
-
- Batlle E, Verdu J, Dominguez D, del Mont M, Llosad, Diaz V, Loukili N, Paciucci R, Alameda F, de Herreros AG. Protein kinase C-alpha activity inversely modulates invasion and growth of intestinal cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:15091–15098. - PubMed
-
- Bazzoni G, Hemler ME. Are changes in integrin affinity and conformation overemphasized? . Trends Biochem Sci. 1998;23:30–34. - PubMed
-
- Burridge K, Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M. Focal adhesions, contractility, and signaling. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1996;12:463–519. - PubMed
-
- Chan BM, Kassner PD, Schiro JA, Byers HR, Kupper TS, Hemler ME. Distinct cellular functions mediated by different VLA integrin α subunit cytoplasmic domains. Cell. 1992;68:1051–1060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

