The effect of cyclopiazonic acid on excitation-contraction coupling in guinea-pig ureteric smooth muscle: role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 10358124
- PMCID: PMC2269382
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0855s.x
The effect of cyclopiazonic acid on excitation-contraction coupling in guinea-pig ureteric smooth muscle: role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
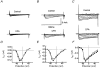
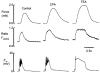
1. We have investigated the effect of cyclopiazonic acid (CPA), an inhibitor of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+-ATPase on excitation-contraction (EC) coupling in guinea-pig ureter, by measuring membrane currents, action potentials, intracellular [Ca2+] and force. 2. CPA (20 micrometers) significantly enhanced the amplitude and duration of phasic contractions of ureteric smooth muscle associated with action potentials. This was accompanied by an increase in the duration of the intracellular Ca2+ transient in intact tissue and single cells but not their amplitude. However, CPA also slowed the rate of rise, and fall, of the force 1|1|Phiand1Phi Ca2+ transients. 3. Membrane potential recordings showed that CPA produced a small depolarization and a large increase in the duration of the plateau phase of the action potential. 4. Patch-clamp studies showed marked inhibition of outward potassium current in the presence of CPA and an inhibition of spontaneous transient outward currents (STOCs). CPA had no effect on inward Ca2+ current. 5. These data suggest that the SR plays a major role in modulating the excitability of the ureter, particularly via curtailing the action potential duration. This in turn will shorten the Ca2+ transient and decrease force. This negative action on developed force predominates over any small role it may play in initiating force in the guinea-pig ureter.
Figures





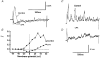

Similar articles
-
Effect of the Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitor, cyclopiazonic acid, on electromechanical coupling in the guinea-pig ureter.Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;114(1):127-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb14916.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 7536095 Free PMC article.
-
Role of intracellular Ca2+ in the K channel opener action of CGRP in the guinea-pig ureter.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Jul;118(6):1493-503. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15565.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8832077 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that a Ca2+ sparks/STOCs coupling mechanism is responsible for the inhibitory effect of caffeine on electro-mechanical coupling in guinea pig ureteric smooth muscle.Cell Calcium. 2007 Sep;42(3):303-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2006.12.005. Epub 2007 Feb 12. Cell Calcium. 2007. PMID: 17298845
-
Sarcoplasmic reticulum function and contractile consequences in ureteric smooth muscles.Novartis Found Symp. 2002;246:208-17; discussion 217-20, 221-7. Novartis Found Symp. 2002. PMID: 12164310 Review.
-
Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Ureteric Smooth Muscle: Mechanisms Driving Ureteric Peristalsis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1124:103-119. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-5895-1_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31183824 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulators of internal Ca2+ stores and the spontaneous electrical and contractile activity of the guinea-pig renal pelvis.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Mar;135(6):1363-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704609. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11906949 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+ entry following P2X receptor activation induces IP3 receptor-mediated Ca2+ release in myocytes from small renal arteries.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Apr;162(7):1618-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01169.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21175582 Free PMC article.
-
On the mechanisms whereby temperature affects excitation-contraction coupling in smooth muscle.J Gen Physiol. 2002 Jan;119(1):93-104. doi: 10.1085/jgp.119.1.93. J Gen Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11773241 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between the action potential, intracellular calcium and force in intact phasic, guinea-pig uretic smooth muscle.J Physiol. 1999 Nov 1;520 Pt 3(Pt 3):867-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00867.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10545150 Free PMC article.
-
The properties of ryanodine-sensitive Ca(2+) release in mouse gastric smooth muscle cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 May;133(1):125-37. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704048. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11325802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baro I, Eisner DA. The effects of thapsigargin on [Ca2+]i in isolated rat mesenteric artery vascular smooth muscle cells. Pflügers Archiv. 1992;420:115–117. - PubMed
-
- Becker PL, Singer JJ, Walsh JV, Fay FS. Regulation of calcium concentration in voltage clamped smooth muscle cells. Science. 1989;244:211–214. - PubMed
-
- Bourreau J-P, Kwan CY, Daniel EE. Distinct pathways to refill acetylcholine-sensitive internal calcium stores in canine smooth muscle. American Journal of Physiology. 1993;265:C28–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

