Apo E structure determines VLDL clearance and atherosclerosis risk in mice
- PMID: 10359567
- PMCID: PMC408371
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI6172
Apo E structure determines VLDL clearance and atherosclerosis risk in mice
Abstract
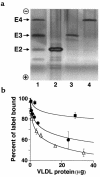
We have generated mice expressing the human apo E4 isoform in place of the endogenous murine apo E protein and have compared them with mice expressing the human apo E3 isoform. Plasma lipid and apolipoprotein levels in the mice expressing only the apo E4 isoform (4/4) did not differ significantly from those in mice with the apo E3 isoform (3/3) on chow and were equally elevated in response to increased lipid and cholesterol in their diet. However, on all diets tested, the 4/4 mice had approximately twice the amount of cholesterol, apo E, and apo B-48 in their VLDL as did 3/3 mice. The 4/4 VLDL competed with human LDL for binding to the human LDL receptor slightly better than 3/3 VLDL, but the VLDL clearance rate in 4/4 mice was half that in 3/3 mice. On an atherogenic diet, there was a trend toward greater atherosclerotic plaque size in 4/4 mice compared with 3/3 mice. These data, together with our earlier observations in wild-type and human APOE*2-replacement mice, demonstrate a direct and highly significant correlation between VLDL clearance rate and mean atherosclerotic plaque size. Therefore, differences solely in apo E protein structure are sufficient to cause alterations in VLDL residence time and atherosclerosis risk in mice.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Defective VLDL metabolism and severe atherosclerosis in mice expressing human apolipoprotein E isoforms but lacking the LDL receptor.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Aug 30;1684(1-3):8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2004.03.004. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15450205
-
Modulation of very low density lipoprotein production and clearance contributes to age- and gender- dependent hyperlipoproteinemia in apolipoprotein E3-Leiden transgenic mice.J Clin Invest. 1996 Mar 1;97(5):1184-92. doi: 10.1172/JCI118532. J Clin Invest. 1996. PMID: 8636429 Free PMC article.
-
[Apolipoprotein E and its alleles in healthy subjects and in atherosclerosis].Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 1998 Nov-Dec;56(6):651-9. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 1998. PMID: 9853024 Review. French.
-
Increased expression of apolipoprotein E in transgenic rabbits results in reduced levels of very low density lipoproteins and an accumulation of low density lipoproteins in plasma.J Clin Invest. 1998 May 15;101(10):2151-64. doi: 10.1172/JCI1599. J Clin Invest. 1998. PMID: 9593771 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoproteins of special significance in atherosclerosis. Insights provided by studies of type III hyperlipoproteinemia.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;454:209-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb11860.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985. PMID: 3000263 Review.
Cited by
-
A Dietary Treatment Improves Cerebral Blood Flow and Brain Connectivity in Aging apoE4 Mice.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:6846721. doi: 10.1155/2016/6846721. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 27034849 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic atherosclerosis in APOE*4 mice: synergy between lipoprotein metabolism and vascular inflammation.J Lipid Res. 2013 Feb;54(2):386-96. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M031435. Epub 2012 Nov 30. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23204275 Free PMC article.
-
ApoE isoform-dependent effects of xanthohumol on high fat diet-induced cognitive impairments and hippocampal metabolic pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 3;13:954980. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.954980. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36278228 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing effects of viral mediated brain expression of apolipoprotein E2 (apoE2) and apoE4 on apoE lipidation and Aβ metabolism in apoE4-targeted replacement mice.Mol Neurodegener. 2015 Mar 5;10:6. doi: 10.1186/s13024-015-0001-3. Mol Neurodegener. 2015. PMID: 25871773 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E allele-dependent pathogenesis: a model for age-related retinal degeneration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Aug 16;102(33):11900-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503015102. Epub 2005 Aug 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16079201 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mahley RW. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with an expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988;240:622–630. - PubMed
-
- Weisgraber KH. Apolipoprotein E: structure-function relationships. Adv Protein Chem. 1994;45:249–302. - PubMed
-
- Kowal RC, et al. Opposing effects of apolipoproteins E and C on lipoprotein binding to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:10771–10779. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T, Bujo H. Close encounters with apolipoprotein E receptors. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1996;7:298–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

