Exocrine pancreatic disorders in transsgenic mice expressing human keratin 8
- PMID: 10359568
- PMCID: PMC408365
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI5343
Exocrine pancreatic disorders in transsgenic mice expressing human keratin 8
Abstract
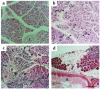
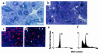
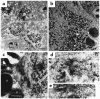
Keratins K8 and K18 are the major components of the intermediate-filament cytoskeleton of simple epithelia. Increased levels of these keratins have been correlated with various tumor cell characteristics, including progression to malignancy, invasive behavior, and drug sensitivity, although a role for K8/K18 in tumorigenesis has not yet been demonstrated. To examine the function of these keratins, we generated mice expressing the human K8 (hk8) gene, which leads to a moderate keratin-content increase in their simple epithelia. These mice displayed progressive exocrine pancreas alterations, including dysplasia and loss of acinar architecture, redifferentiation of acinar to ductal cells, inflammation, fibrosis, and substitution of exocrine by adipose tissue, as well as increased cell proliferation and apoptosis. Histological changes were not observed in other simple epithelia, such as the liver. Electron microscopy showed that transgenic acinar cells have keratins organized in abundant filament bundles dispersed throughout the cytoplasm, in contrast to control acinar cells, which have scarce and apically concentrated filaments. The phenotype found was very similar to that reported for transgenic mice expressing a dominant-negative mutant TGF-beta type II receptor (TGFbetaRII mice). We show that these TGFbetaRII mutant mice also have elevated K8/K18 levels. These results indicate that simple epithelial keratins play a relevant role in the regulation of exocrine pancreas homeostasis and support the idea that disruption of mechanisms that normally regulate keratin expression in vivo could be related to inflammatory and neoplastic pancreatic disorders.
Figures



References
-
- Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller D. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells[review] Cell. 1982;31:11–24. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs E, Weber K. Intermediate filaments: structure, dynamics, function and disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:345–382. - PubMed
-
- McLean WH, Lane EB. Intermediate filaments in disease[review] Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995;7:118–125. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs E. The cytoskeleton and disease: genetic disorders of IFs. Annu Rev Genet. 1996;30:197–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

