Exercise provides direct biphasic cardioprotection via manganese superoxide dismutase activation
- PMID: 10359573
- PMCID: PMC2193084
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.11.1699
Exercise provides direct biphasic cardioprotection via manganese superoxide dismutase activation
Abstract
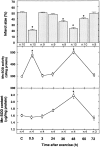
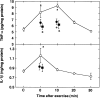
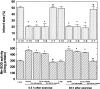
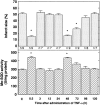
Epidemiologic investigations have shown that exercise reduces morbidity and mortality from coronary artery disease. In this study, using a rat model, we attempted to determine whether exercise can reduce ischemic injury to the heart and elucidate a mechanism for the cardioprotective effect of exercise. Results showed that exercise significantly reduced the magnitude of a myocardial infarction in biphasic manner. The time course for cardioprotection resembled that of the change in manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD) activity. The administration of the antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotide to Mn-SOD abolished the expected decrease in infarct size. We showed that the level of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) increased after exercise. The simultaneous administration of the neutralizing antibodies to the cytokines abolished the exercise-induced cardioprotection and the activation of Mn-SOD. Furthermore, TNF-alpha can mimic the biphasic pattern of cardioprotection and activation of Mn-SOD. An antioxidant completely abolished cardioprotection and the activation of Mn-SOD by exercise or the injection of TNF-alpha as well as exercise-induced increase in TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. The production of reactive oxygen species and endogenous TNF-alpha and IL-1beta induced by exercise leads to the activation of Mn-SOD, which plays major roles in the acquisition of biphasic cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats.
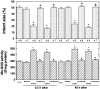
Figures

References
-
- Fletcher GF, Blair SN, Blumenthal J, Caspersen C, Chaitman B, Epstein S, Falls H, Froelicher ES, Froelicher VF, Pina IL. Statement on exercise. Benefits and recommendations for physical activity programs for all Americans. A statement for health professionals by the Committee on Exercise and Cardiac Rehabilitation of the Council on Clinical Cardiology, American Heart Association. Circulation. 1992;86:340–344. - PubMed
-
- Laughlin MH, McAllister RM. Exercise training-induced coronary vascular adaptation. J Appl Physiol. 1992;73:2209–2225. - PubMed
-
- Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74:1124–1136. - PubMed
-
- Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. New insights into potential mechanisms of ischemic preconditioning. Circulation. 1991;84:442–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

