Acquisition of selectin binding and peripheral homing properties by CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells
- PMID: 10359580
- PMCID: PMC2193075
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.11.1765
Acquisition of selectin binding and peripheral homing properties by CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells
Abstract
Different T cell subsets exhibit distinct capacities to migrate into peripheral sites of inflammation, and this may in part reflect differential expression of homing receptors and chemokine receptors. Using an adoptive transfer approach, we examined the ability of functionally distinct subsets of T cells to home to a peripheral inflammatory site. The data directly demonstrate the inability of naive T cells and the ability of effector cells to home to inflamed peritoneum. Furthermore, interleukin (IL)-12 directs the differentiation of either CD4(+) or CD8(+) T cells into effector populations that expresses functional E- and P-selectin ligand and that are preferentially recruited into the inflamed peritoneum compared with T cells differentiated in the presence of IL-4. Recruitment can be blocked by anti-E- and -P-selectin antibodies. The presence of antigen in the peritoneum promotes local proliferation of recruited T cells, and significantly amplifies the Th1 polarization of the lymphocytic infiltrate. Preferential recruitment of Th1 cells into the peritoneum is also seen when cytokine response gene 2 (CRG-2)/interferon gamma-inducible protein 10 (IP-10) is used as the sole inflammatory stimulus. We have also found that P-selectin binds only to antigen-specific T cells in draining lymph nodes after immunization, implying that both antigen- and cytokine-mediated signals are required for expression of functional selectin-ligand.
Figures
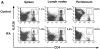


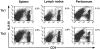

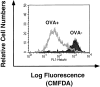







Similar articles
-
Expression of functional selectin ligands on Th cells is differentially regulated by IL-12 and IL-4.J Immunol. 1999 Mar 15;162(6):3193-201. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10092770
-
CD4+ T cells migrate into inflamed skin only if they express ligands for E- and P-selectin.J Immunol. 1998 Jul 15;161(2):963-70. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9670976
-
P-, E-, and L-selectin mediate migration of activated CD8+ T lymphocytes into inflamed skin.J Immunol. 2002 Oct 15;169(8):4307-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.8.4307. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12370362
-
Th1/Th2 subsets: distinct differences in homing and chemokine receptor expression?Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1999;21(3):263-85. doi: 10.1007/BF00812257. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1999. PMID: 10666773 Review.
-
Differential migration of Th1 and Th2 cells--implications for vaccine and infection studies.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1998 May 15;63(1-2):157-66. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(98)00092-0. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1998. PMID: 9656451 Review.
Cited by
-
Left Ventricular T-Cell Recruitment Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Heart Failure.Circ Heart Fail. 2015 Jul;8(4):776-87. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.002225. Epub 2015 May 28. Circ Heart Fail. 2015. PMID: 26022677 Free PMC article.
-
Differential polarization of immune responses by genetic cotransfer of chemokines changes the protective immunity of DNA vaccine against pseudorabies virus.Immunology. 2007 Feb;120(2):182-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02490.x. Epub 2006 Nov 20. Immunology. 2007. PMID: 17116174 Free PMC article.
-
Ex vivo stimulation of cord blood mononuclear cells by dexamethasone and interleukin-7 results in the maturation of interferon-gamma-secreting effector memory T cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Sep;141(3):440-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02863.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16045733 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 controls chemokine production and T helper cell type 2 cell trafficking in allergic pulmonary inflammation.J Exp Med. 2001 May 7;193(9):1087-96. doi: 10.1084/jem.193.9.1087. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11342593 Free PMC article.
-
Sialyl-LewisX Glycoantigen Is Enriched on Cells with Persistent HIV Transcription during Therapy.Cell Rep. 2020 Aug 4;32(5):107991. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107991. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32755584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tietz W, Allemand Y, Borges E, von Laer D, Hallmann R, Vestweber D, Hamann A. CD4+T cells migrate into inflamed skin only if they express ligands for E- and P-selectin. J Immunol. 1998;161:963–970. - PubMed
-
- Bradley LM, Watson SR. Lymphocyte migration into tissue: the paradigm derived from CD4 subsets. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:312–320. - PubMed
-
- Mackay CR, Marston W, Dudler L. Altered patterns of T cell migration through lymph nodes and skin following antigen challenge. Eur J Immunol. 1992;22:2205–2210. - PubMed
-
- Swain SL, Bradley LM. Helper T cell memory: more questions than answers. Semin Immunol. 1992;4:59–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

