MD-2, a molecule that confers lipopolysaccharide responsiveness on Toll-like receptor 4
- PMID: 10359581
- PMCID: PMC2193086
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.11.1777
MD-2, a molecule that confers lipopolysaccharide responsiveness on Toll-like receptor 4
Abstract
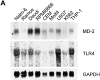
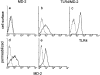
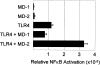
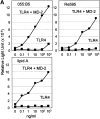
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is a mammalian homologue of Drosophila Toll, a leucine-rich repeat molecule that can trigger innate responses against pathogens. The TLR4 gene has recently been shown to be mutated in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice, both of which are low responders to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). TLR4 may be a long-sought receptor for LPS. However, transfection of TLR4 does not confer LPS responsiveness on a recipient cell line, suggesting a requirement for an additional molecule. Here, we report that a novel molecule, MD-2, is requisite for LPS signaling of TLR4. MD-2 is physically associated with TLR4 on the cell surface and confers responsiveness to LPS. MD-2 is thus a link between TLR4 and LPS signaling. Identification of this new receptor complex has potential implications for understanding host defense, as well as pathophysiologic, mechanisms.
Figures

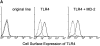
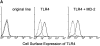

References
-
- Hammond-Kosak KE, Jones JDG. Plant disease resistance genes. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1997;48:575–607. - PubMed
-
- Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart J-M, Hoffmann JA. The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spaetzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophilaadults. Cell. 1996;86:973–983. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway CA., Jr Innate immunity: impact on the adaptive immune response. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:4–9. - PubMed
-
- Vogel G. Fly development genes lead to immune find. Science. 1998;281:1942–1944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

