The IKKbeta subunit of IkappaB kinase (IKK) is essential for nuclear factor kappaB activation and prevention of apoptosis
- PMID: 10359587
- PMCID: PMC2193082
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.11.1839
The IKKbeta subunit of IkappaB kinase (IKK) is essential for nuclear factor kappaB activation and prevention of apoptosis
Abstract
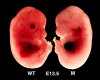
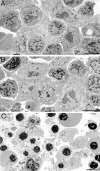
The IkappaB kinase (IKK) complex is composed of three subunits, IKKalpha, IKKbeta, and IKKgamma (NEMO). While IKKalpha and IKKbeta are highly similar catalytic subunits, both capable of IkappaB phosphorylation in vitro, IKKgamma is a regulatory subunit. Previous biochemical and genetic analyses have indicated that despite their similar structures and in vitro kinase activities, IKKalpha and IKKbeta have distinct functions. Surprisingly, disruption of the Ikkalpha locus did not abolish activation of IKK by proinflammatory stimuli and resulted in only a small decrease in nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activation. Now we describe the pathophysiological consequence of disruption of the Ikkbeta locus. IKKbeta-deficient mice die at mid-gestation from uncontrolled liver apoptosis, a phenotype that is remarkably similar to that of mice deficient in both the RelA (p65) and NF-kappaB1 (p50/p105) subunits of NF-kappaB. Accordingly, IKKbeta-deficient cells are defective in activation of IKK and NF-kappaB in response to either tumor necrosis factor alpha or interleukin 1. Thus IKKbeta, but not IKKalpha, plays the major role in IKK activation and induction of NF-kappaB activity. In the absence of IKKbeta, IKKalpha is unresponsive to IKK activators.
Figures




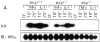
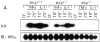
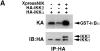
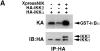
References
-
- Baldwin AS. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–681. - PubMed
-
- May MJ, Ghosh S. Signal transduction through NF-κB. Immunol Today. 1998;19:80–88. - PubMed
-
- Brown K, Gerstberger S, Carlson L, Franzoso G, Siebenlist U. Control of IκBα proteolysis by site-specific, signal-induced phosphorylation. Science. 1995;267:1485–1491. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Hagler J, Palombella VJ, Melandri F, Scherer D, Ballard D, Maniatis T. Signal-induced site-specific phosphorylation targets IκB to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1586–1597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

