Membrane tubule-mediated reassembly and maintenance of the Golgi complex is disrupted by phospholipase A2 antagonists
- PMID: 10359595
- PMCID: PMC25369
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.6.1763
Membrane tubule-mediated reassembly and maintenance of the Golgi complex is disrupted by phospholipase A2 antagonists
Abstract
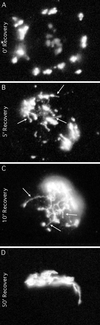
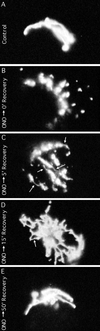
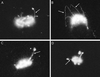
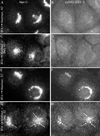
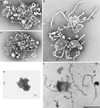
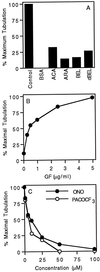
Although membrane tubules can be found extending from, and associated with, the Golgi complex of eukaryotic cells, their physiological function has remained unclear. To gain insight into the biological significance of membrane tubules, we have developed methods for selectively preventing their formation. We show here that a broad range of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) antagonists not only arrest membrane tubule-mediated events that occur late in the assembly of the Golgi complex but also perturb its normal steady-state tubulovesicular architecture by inducing a reversible fragmentation into separate "mini-stacks." In addition, we show that these same compounds prevent the formation of membrane tubules from Golgi stacks in an in vitro reconstitution system. This in vitro assay was further used to demonstrate that the relevant PLA2 activity originates from the cytoplasm. Taken together, these results demonstrate that Golgi membrane tubules, sensitive to potent and selective PLA2 antagonists, mediate both late events in the reassembly of the Golgi complex and the dynamic maintenance of its steady-state architecture. In addition, they implicate a role for cytoplasmic PLA2 enzymes in mediating these membrane trafficking events.
Figures
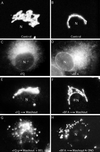
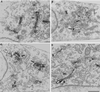
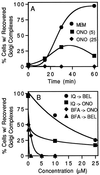
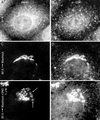
References
-
- Acharya U, Jacobs R, Peters JM, Watson N, Farquhar MG, Malhotra V. The formation of Golgi stacks from vesiculated Golgi membranes requires two distinct fusion events. Cell. 1995a;82:895–904. - PubMed
-
- Ackermann EJ, Conde-Frieboes K, Dennis EA. Inhibition of macrophage Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 by bromoenol lactone and Trifluoromethyl ketones. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:445–450. - PubMed
-
- Balboa MA, Balsinde J, Jones SS, Dennis EA. Identity between the Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 enzymes from P388D1 macrophages and Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:8576–8580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

