The PDZ domain of the LIM protein enigma binds to beta-tropomyosin
- PMID: 10359609
- PMCID: PMC25398
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.6.1973
The PDZ domain of the LIM protein enigma binds to beta-tropomyosin
Abstract
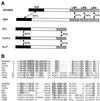
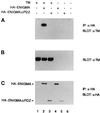
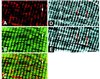
PDZ and LIM domains are modular protein interaction motifs present in proteins with diverse functions. Enigma is representative of a family of proteins composed of a series of conserved PDZ and LIM domains. The LIM domains of Enigma and its most related family member, Enigma homology protein, bind to protein kinases, whereas the PDZ domains of Enigma and family member actin-associated LIM protein bind to actin filaments. Enigma localizes to actin filaments in fibroblasts via its PDZ domain, and actin-associated LIM protein binds to and colocalizes with the actin-binding protein alpha-actinin-2 at Z lines in skeletal muscle. We show that Enigma is present at the Z line in skeletal muscle and that the PDZ domain of Enigma binds to a skeletal muscle target, the actin-binding protein tropomyosin (skeletal beta-TM). The interaction between Enigma and skeletal beta-TM was specific for the PDZ domain of Enigma, was abolished by mutations in the PDZ domain, and required the PDZ-binding consensus sequence (Thr-Ser-Leu) at the extreme carboxyl terminus of skeletal beta-TM. Enigma interacted with isoforms of tropomyosin expressed in C2C12 myotubes and formed an immunoprecipitable complex with skeletal beta-TM in transfected cells. The association of Enigma with skeletal beta-TM suggests a role for Enigma as an adapter protein that directs LIM-binding proteins to actin filaments of muscle cells.
Figures




References
-
- Agulnick AD, Tiara M, Breen JJ, Tanaka T, Dawid IB, Westphal H. Interactions of the LIM-domain-binding factor Ldb1 with LIM homeodomain proteins. Nature. 1996;384:270–272. - PubMed
-
- Angerer RC, Stoler MH, Angerer RC. In situ hybridization with RNA probes—an annotated recipe. In: Valentino KL, Eberwine JH, Barchas JD, editors. In Situ Hybridization—Applications to Neurobiology. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1987. pp. 71–96.
-
- Arber S, Halder G, Caroni P. Muscle LIM protein, a novel essential regulator of myogenesis, promotes myogenic differentiation. Cell. 1994;79:221–231. - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Caroni P. Specificity of single LIM motifs in targeting and LIM/LIM interactions in situ. Genes & Dev. 1996;10:289–300. - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Hunter JJ, Ross J, Jr, Hongo M, Sansig G, Borg J, Perriard J-C, Chien KR, Caroni P. MLP-deficient mice exhibit a disruption of cardiac cytoarchitectural organization, dilated cardiomyopathy, and heart failure. Cell. 1997;88:393–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

