Vimentin dephosphorylation by protein phosphatase 2A is modulated by the targeting subunit B55
- PMID: 10359611
- PMCID: PMC25403
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.6.1997
Vimentin dephosphorylation by protein phosphatase 2A is modulated by the targeting subunit B55
Abstract
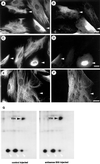
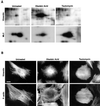
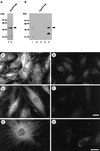
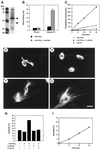
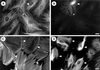
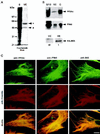
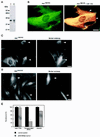
The intermediate filament protein vimentin is a major phosphoprotein in mammalian fibroblasts, and reversible phosphorylation plays a key role in its dynamic rearrangement. Selective inhibition of type 2A but not type 1 protein phosphatases led to hyperphosphorylation and concomitant disassembly of vimentin, characterized by a collapse into bundles around the nucleus. We have analyzed the potential role of one of the major protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulatory subunits, B55, in vimentin dephosphorylation. In mammalian fibroblasts, B55 protein was distributed ubiquitously throughout the cytoplasm with a fraction associated to vimentin. Specific depletion of B55 in living cells by antisense B55 RNA was accompanied by disassembly and increased phosphorylation of vimentin, as when type 2A phosphatases were inhibited using okadaic acid. The presence of B55 was a prerequisite for PP2A to efficiently dephosphorylate vimentin in vitro or to induce filament reassembly in situ. Both biochemical fractionation and immunofluorescence analysis of detergent-extracted cells revealed that fractions of PP2Ac, PR65, and B55 were tightly associated with vimentin. Furthermore, vimentin-associated PP2A catalytic subunit was displaced in B55-depleted cells. Taken together these data show that, in mammalian fibroblasts, the intermediate filament protein vimentin is dephosphorylated by PP2A, an event targeted by B55.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of protein phosphatase 2A with its substrate vimentin intermediate filaments in 9L rat brain tumor cells.J Cell Biochem. 2000 Jul 19;79(1):126-38. J Cell Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10906761
-
Differential inhibition and posttranslational modification of protein phosphatase 1 and 2A in MCF7 cells treated with calyculin-A, okadaic acid, and tautomycin.J Biol Chem. 1997 May 23;272(21):13856-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.21.13856. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9153244
-
Vimentin is hyperphosphorylated in primary human fibroblasts treated with okadaic acid.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):1165-70. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90662-q. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991. PMID: 1647766
-
[Tumor promotion by inhibitors of protein phosphatase 1 and 2A].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1998 Jun;43(8 Suppl):1102-10. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1998. PMID: 9655968 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
A pharmacophore model of tautomycin, an inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1997 Oct;50(10):801-7. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.50.801. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1997. PMID: 9402983 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A mammalian homolog of yeast MOB1 is both a member and a putative substrate of striatin family-protein phosphatase 2A complexes.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 29;276(26):24253-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102398200. Epub 2001 Apr 23. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11319234 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of vascular endothelial cadherin controls lymphocyte emigration.J Cell Sci. 2008 Jan 1;121(Pt 1):29-37. doi: 10.1242/jcs.022681. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18096689 Free PMC article.
-
Functional cdc25C dual-specificity phosphatase is required for S-phase entry in human cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Jul;14(7):2984-98. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-08-0515. Epub 2003 Apr 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12857880 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatases 1 and 2A transiently associate with myosin during the peak rate of secretion from mast cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Mar;13(3):1083-98. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-12-0587. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 11907284 Free PMC article.
-
Altered phosphorylation and distribution status of vimentin in rat seminiferous epithelium following 17β-estradiol treatment.Histochem Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;136(5):543-55. doi: 10.1007/s00418-011-0856-5. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Histochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21915674
References
-
- Agostinis P, Goris J, Waelkens E, Pinna LA, Marchiori F, Merlevede W. Dephosphorylation of phosphoproteins and synthetic phosphopeptides. Study of the specificity of the polycation-stimulated and Mg-ATP-dependent phosphorylase phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:1060–1064. - PubMed
-
- Blattler DP, Garner F, Van Slyke K, Bradley A. Quantitative electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels of 2–40% J Chromatogr. 1972;64:147–155.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

