Signaling via beta1 integrins and mitogen-activated protein kinase determines human epidermal stem cell fate in vitro
- PMID: 10359780
- PMCID: PMC21983
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6728
Signaling via beta1 integrins and mitogen-activated protein kinase determines human epidermal stem cell fate in vitro
Abstract
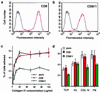
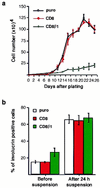
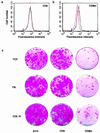
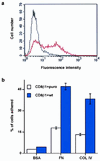
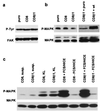
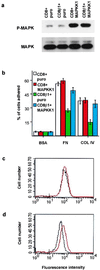
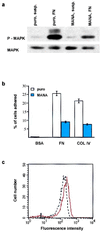
Human epidermal stem cells express higher levels of beta1 integrins and are more adhesive than keratinocytes that are destined to differentiate. To investigate whether high beta1 integrin expression and adhesiveness are essential for maintaining keratinocytes in the stem cell compartment, we introduced a dominant-negative beta1 integrin mutant, CD8beta1, into cultured human keratinocytes, thereby interfering with beta1 integrin function. Surface beta1 integrin levels, adhesiveness, and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase activation on fibronectin were reduced, and exit from the stem cell compartment was stimulated. Adhesiveness and proliferative potential were restored by overexpressing wild-type beta1 integrin or by constitutive MAP kinase activation. Conversely, a dominant-negative MAP kinase kinase 1 mutant decreased adhesiveness and stem cell number in the absence of CD8beta1. MAP kinase activation by alpha6beta4-mediated adhesion and mitogens was normal in CD8beta1 cells, and constitutive MAP kinase activation did not affect adhesion and proliferation of control keratinocytes. We conclude that beta1 integrins and MAP kinase cooperate to maintain the epidermal stem cell compartment in vitro.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

