Tumor necrosis factor alpha is a key component in the obesity-linked elevation of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1
- PMID: 10359811
- PMCID: PMC22014
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6902
Tumor necrosis factor alpha is a key component in the obesity-linked elevation of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1
Abstract
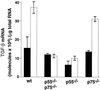
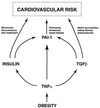
Obesity is associated with a cluster of abnormalities, including hypertension, insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and elevated levels of both plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta). Although these changes may increase the risk for accelerated atherosclerosis and fatal myocardial infarction, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain to be defined. Although tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) has been implicated in the insulin resistance associated with obesity, its role in other disorders of obesity is largely unknown. In this report, we show that in obese (ob/ob) mice, neutralization of TNF-alpha or deletion of both TNF receptors (TNFRs) results in significantly reduced levels of plasma PAI-1 antigen, plasma insulin, and adipose tissue PAI-1 and TGF-beta mRNAs. Studies in which exogenous TNF-alpha was infused into lean mice lacking individual TNFRs indicate that TNF-alpha signaling of PAI-1 in adipose tissue can be mediated by either the p55 or the p75 TNFR. However, TNF-alpha signaling of TGF-beta mRNA expression in adipose tissue is mediated exclusively via the p55 TNFR. Our results suggest that TNF-alpha is a common link between the insulin resistance and elevated PAI-1 and TGF-beta in obesity. The chronic elevation of TNF-alpha in obesity thus may directly promote the development of the complex cardiovascular risk profile associated with this condition.
Figures
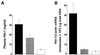

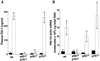


References
-
- Hjermann I. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992;8:S5–S10. - PubMed
-
- Finer N. Br Med Bull. 1997;53:229–450. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen S, Jensen M D. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1997;8:200–204. - PubMed
-
- Björntorp P. Ann Med. 1992;24:15–18. - PubMed
-
- Hotamisligil G S, Shargill N S, Spiegelman B M. Science. 1993;259:87–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

