Multiple event activation of a generic prodrug trigger by antibody catalysis
- PMID: 10359815
- PMCID: PMC22018
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6925
Multiple event activation of a generic prodrug trigger by antibody catalysis
Abstract
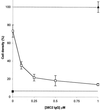
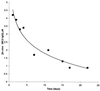
Chemotherapeutic regimes are typically limited by nonspecific toxicity. To address this problem we have developed a broadly applicable drug-masking chemistry that operates in conjunction with a unique broad-scope catalytic antibody. This masking chemistry is applicable to a wide range of drugs because it is compatible with virtually any heteroatom. We demonstrate that generic drug-masking groups may be selectively removed by sequential retro-aldol-retro-Michael reactions catalyzed by antibody 38C2. This reaction cascade is not catalyzed by any known natural enzyme. Application of this masking chemistry to the anticancer drugs doxorubicin and camptothecin produced prodrugs with substantially reduced toxicity. These prodrugs are selectively unmasked by the catalytic antibody when it is applied at therapeutically relevant concentrations. We have demonstrated the efficacy of this approach by using human colon and prostate cancer cell lines. The antibody demonstrated a long in vivo half-life after administration to mice. Based on these findings, we believe that the system described here has the potential to become a key tool in selective chemotherapeutic strategies.
Figures
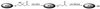

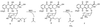



Similar articles
-
In vivo activity in a catalytic antibody-prodrug system: Antibody catalyzed etoposide prodrug activation for selective chemotherapy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jun 19;98(13):7528-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.131187998. Epub 2001 Jun 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11404472 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactivation of self-immolative dendritic prodrugs by catalytic antibody 38C2.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Feb 18;126(6):1726-31. doi: 10.1021/ja039052p. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 14871103
-
A prodrug nanoassembly entrapping drugs as a tumor-targeted delivery system.Chem Commun (Camb). 2013 Jan 28;49(8):801-3. doi: 10.1039/c2cc37798e. Chem Commun (Camb). 2013. PMID: 23235958
-
15 years of ATTEMPTS: a macromolecular drug delivery system based on the CPP-mediated intracellular drug delivery and antibody targeting.J Control Release. 2015 May 10;205:58-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 4. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 25483423 Review.
-
Painting the target around the arrow: two-step prodrug therapies from a carbohydrate chemist's perspective.Curr Drug Deliv. 2007 Oct;4(4):264-8. doi: 10.2174/156720107782151278. Curr Drug Deliv. 2007. PMID: 17979645 Review.
Cited by
-
Instant immunity through chemically programmable vaccination and covalent self-assembly.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 17;106(11):4378-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900147106. Epub 2009 Mar 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19255430 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the concept of chemically programmable antibodies to RNA aptamers: chemically programmed biotherapeutics.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010 Aug 9;49(34):5934-7. doi: 10.1002/anie.201001736. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010. PMID: 20645365 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo activity in a catalytic antibody-prodrug system: Antibody catalyzed etoposide prodrug activation for selective chemotherapy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jun 19;98(13):7528-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.131187998. Epub 2001 Jun 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11404472 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and activities of macromolecule conjugates of the CCR5 antagonist Maraviroc.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2014 Feb 13;5(2):133-137. doi: 10.1021/ml400370w. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 24563723 Free PMC article.
-
Chemically programmed monoclonal antibodies for cancer therapy: adaptor immunotherapy based on a covalent antibody catalyst.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 29;100(9):5396-400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0931308100. Epub 2003 Apr 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12702756 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

