Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) transcription and translation in the CD4+ T cell-transplanted scid mouse model of colitis
- PMID: 10361228
- PMCID: PMC1905296
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00915.x
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) transcription and translation in the CD4+ T cell-transplanted scid mouse model of colitis
Abstract
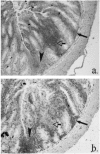
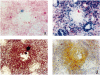
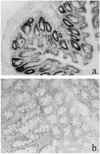
The adoptive transfer of activated CD4+ alpha/beta T cell blasts from the spleens of immunocompetent C.B-17+/+ or BALB/cdm2 mice into C.B-17scid/scid (scid) mice induces a colitis in the scid recipient within 8 weeks, which progresses to severe disease within 16 weeks. T cells isolated from recipient colon show a Th1 cytokine phenotype. We have examined the relationship between the phenotype of the cellular infiltrate and the transcription and translation of the proinflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha. The techniques of double indirect immunohistology and in situ hybridization using digoxigenin-labelled riboprobes were used. The prominent myeloid cell infiltrate in diseased tissues comprised F4/80+, Mac-l+ macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells and activated macrophages. TNF-alpha transcription and translation were associated with activated macrophages in the lamina propria. Activated macrophages transcribing and translating TNF-alpha were clustered in areas of tissue destruction. Crypt epithelium of inflamed tissues transcribed TNF-alpha at a very early stage of the disease process, but translation of TNF-alpha protein could only be found in advanced epithelial dysplasia. This indicates differential post-transcriptional control of TNF-alpha in activated macrophages and the epithelium.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of selectin-binding epitopes and cytokines by CD4+ T cells repopulating scid mice with colitis.Eur J Immunol. 1998 Jun;28(6):1785-97. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199806)28:06<1785::AID-IMMU1785>3.0.CO;2-Y. Eur J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9645359
-
Polyclonal expansion of adoptively transferred CD4+ alpha beta T cells in the colonic lamina propria of scid mice with colitis.Eur J Immunol. 1996 May;26(5):1156-63. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260529. Eur J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8647181
-
Colitis-inducing potency of CD4+ T cells in immunodeficient, adoptive hosts depends on their state of activation, IL-12 responsiveness, and CD45RB surface phenotype.J Immunol. 1999 Mar 15;162(6):3702-10. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10092833
-
Cytotoxic reactivity of gut lamina propria CD4+ alpha beta T cells in SCID mice with colitis.Eur J Immunol. 1996 Dec;26(12):3074-83. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830261238. Eur J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8977307
-
A new model of chronic colitis in SCID mice induced by adoptive transfer of CD62L+ CD4+ T cells: insights into the regulatory role of interleukin-6 on apoptosis.Pathobiology. 2002-2003;70(3):170-6. doi: 10.1159/000068150. Pathobiology. 2002. PMID: 12571422
Cited by
-
The role of up-regulated serine proteases and matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of a murine model of colitis.Am J Pathol. 2000 Dec;157(6):1927-35. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64831-6. Am J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 11106565 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of T-regulatory cells, induced by immature dendritic cells, which inhibit enteroantigen-reactive colitis-inducing T-cell responses in vitro and in vivo.Immunology. 2004 Dec;113(4):499-508. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01977.x. Immunology. 2004. PMID: 15554928 Free PMC article.
-
Allicin attenuates inflammation and suppresses HLA-B27 protein expression in ankylosing spondylitis mice.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:171573. doi: 10.1155/2013/171573. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24324956 Free PMC article.
-
Dual TNF-α/IL-12p40 Interference as a Strategy to Protect Against Colitis Based on miR-16 Precursors With Macrophage Targeting Vectors.Mol Ther. 2015 Oct;23(10):1611-21. doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.111. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Mol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26073885 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage Identification In Situ.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 4;9(10):1393. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101393. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680510 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sadlack B, Merz H, Schorle H, Schimpl A, Feller AC, Horak I. Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell. 1993;75:253–61. - PubMed
-
- Kühn RL, Löhler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, Müller W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell. 1993;75:263–14. - PubMed
-
- Mombaerts P, Mizoguchi E, Grusby MJ, Glimcher LH, Bhan AK, Tonegawa S. Spontaneous development of inflammatory bowel disease in T cell receptor mutant mice. Cell. 1993;75:275–82. - PubMed
-
- Hornquist CE, Lu X, Rogers-Fani PM, Rudolph U, Shappell S, Birnbaumer L, Harriman GR. Gαi2-deficient mice with colitis exhibit a local increase in memory CD4+T cells and proinflammatory Th1-type cytokines. J Immunol. 1997;158:1068–77. - PubMed
-
- Morrissey PJ, Charrier K, Braddy S, Liggitt D, Watson JD. CD4+ T cells that express high levels of CD45RB induce wasting disease when transferred into congenic severe combined immunodeficient mice. Disease development is prevented by co-transfer of purified CD4+T cells. J Exp Med. 1993;178:237–44. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

