Histological damage in chronic hepatitis C is not related to the extent of infection in the liver
- PMID: 10362814
- PMCID: PMC1866612
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65445-4
Histological damage in chronic hepatitis C is not related to the extent of infection in the liver
Abstract
It has not been completely elucidated whether the liver injury induced by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) is due to direct cytopathic damage or to an immune-mediated response against HCV-infected hepatocytes. In this work, we have determined the percentage of HCV-infected hepatocytes, the histological activity index, and the viremia levels in chronically HCV-infected patients with different grades of liver injury to investigate any possible correlation between them. For that purpose, liver biopsies from 27 patients with HCV chronic hepatitis were analyzed by in situ hybridization. This technique revealed that the percentage of infected hepatocytes ranged from 0.04% to 83.6%. Regarding the viremia levels, HCV RNA concentration ranged from 1.8 x 10(3) to 1.4 x 10(6) genome copies/ml. A significant correlation (r = 0.54; P = 0.003) between the percentage of infected hepatocytes and the viremia levels was found. In contrast, no correlation was observed between the percentage of HCV-infected hepatocytes or the viremia levels and the histological activity index. In conclusion, we have shown that the HCV viremia reflects the extent of the infection in the liver and that the liver injury in chronic HCV infection is not directly related to either the number of infected hepatocytes or the serum HCV RNA concentration.
Figures
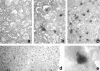
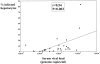

Similar articles
-
Distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in liver biopsies from children and adults with chronic hepatitis C.J Med Virol. 2001 May;64(1):1-5. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1009. J Med Virol. 2001. PMID: 11285561
-
Phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis C virus isolates and their correlation to viremia, liver function tests, and histology.Hepatology. 1996 Nov;24(5):1003-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240505. Hepatology. 1996. PMID: 8903367
-
Intrahepatic hepatitis C virus RNA quantification in microdissected hepatocytes.J Hepatol. 2004 Apr;40(4):682-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2003.12.012. J Hepatol. 2004. PMID: 15030986
-
Pathogenesis of hepatocellular damage in chronic hepatitis C virus infection.Clin Liver Dis. 1997 Nov;1(3):515-28, v. doi: 10.1016/s1089-3261(05)70318-4. Clin Liver Dis. 1997. PMID: 15560055 Review.
-
Histopathology of HCV infection.Clin Liver Dis. 1997 Nov;1(3):529-41, vi. doi: 10.1016/s1089-3261(05)70319-6. Clin Liver Dis. 1997. PMID: 15560056 Review.
Cited by
-
Intrahepatic hepatitis C virus replication correlates with chronic hepatitis C disease severity in vivo.J Virol. 2006 Mar;80(5):2280-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.5.2280-2290.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16474135 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of hepatitis C virus (HCV) negative strand RNA and NS3 protein in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC): CD3+, CD14+ and CD19+.Virol J. 2013 Nov 26;10:346. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-346. Virol J. 2013. PMID: 24279719 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic hepatitis C.Gut Liver. 2011 Jun;5(2):117-32. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2011.5.2.117. Epub 2011 Jun 24. Gut Liver. 2011. PMID: 21814590 Free PMC article.
-
Percentage of hepatitis C virus-infected hepatocytes is a better predictor of response than serum viremia levels.J Mol Diagn. 2005 Oct;7(4):535-43. doi: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60585-5. J Mol Diagn. 2005. PMID: 16237224 Free PMC article.
-
Ultracentrifugation of serum samples allows detection of hepatitis C virus RNA in patients with occult hepatitis C.J Virol. 2007 Jul;81(14):7710-5. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02750-06. Epub 2007 May 2. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17475654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shindo M, Di Bisceglie AM, Biswas R, Mihalik K, Feinstone SM: Hepatitis C virus replication during acute infection in the chimpanzee. J Infect Dis 1992, 166:424-427 - PubMed
-
- Kato N, Yokosuka O, Hosoda K, Ito Y, Onto M, Omata M: Quantification of hepatitis C virus by competitive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction: increase of the virus in advanced liver disease. Hepatology 1993, 18:16-20 - PubMed
-
- Yuki N, Hayashi N, Kamada T: HCV viraemia and liver injury in symptom-free blood donors [letter]. Lancet 1993, 342:444 - PubMed
-
- Di Bisceglie AM, Hoofnagle JH, Krawczynski K: Changes in hepatitis C virus antigen in liver with antiviral therapy. Gastroenterology 1993, 105:858-862 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

