Induction of AIDS in rhesus monkeys by a recombinant simian immunodeficiency virus expressing nef of human immunodeficiency virus type 1
- PMID: 10364333
- PMCID: PMC112642
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.7.5814-5825.1999
Induction of AIDS in rhesus monkeys by a recombinant simian immunodeficiency virus expressing nef of human immunodeficiency virus type 1
Abstract
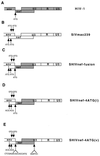
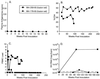
A nef gene is present in all primate lentiviruses, including human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and simian immunodeficiency virus of macaque monkeys (SIVmac). However, the nef genes of HIV-1 and SIVmac exhibit minimal sequence identity, and not all properties are shared by the two. Nef sequences of SIVmac239 were replaced by four independent nef alleles of HIV-1 in a context that was optimal for expression. The sources of the HIV-1 nef sequences included NL 4-3, a variant NL 4-3 gene derived from a recombinant-infected rhesus monkey, a patient nef allele, and a nef consensus sequence. Of 16 rhesus monkeys infected with these SHIVnef chimeras, 9 maintained high viral loads for prolonged periods, as observed with the parental SIVmac239, and 6 have died with AIDS 52 to 110 weeks postinfection. Persistent high loads were observed at similar frequencies with the four different SIV recombinants that expressed these independent HIV-1 nef alleles. Infection with other recombinant SHIVnef constructions resulted in sequence changes in infected monkeys that either created an open nef reading frame or optimized the HIV-1 nef translational context. The HIV-1 nef gene was uniformly retained in all SHIVnef-infected monkeys. These results demonstrate that HIV-1 nef can substitute for SIVmac nef in vivo to produce a pathogenic infection. However, the model suffers from an inability to consistently obtain persisting high viral loads in 100% of the infected animals, as is observed with the parental SIVmac239.
Figures











References
-
- Aiken C, Konner J, Landau N, Lenburg M E, Trono D. Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane-proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1994;76:853–864. - PubMed
-
- Alexander L, Veazey R S, Czajak S, DeMaria M, Rosenzweig M, Lackner A A, Desrosiers R C, Sasseville V G. Recombinant simian immunodeficiency virus expressing green fluorescent protein identifies infected cells in rhesus monkeys. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1999;15:11–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

