Purification and characterization of caffeine synthase from tea leaves
- PMID: 10364410
- PMCID: PMC59297
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.120.2.579
Purification and characterization of caffeine synthase from tea leaves
Abstract
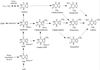
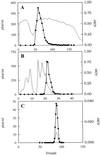
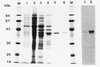
Caffeine synthase (CS), the S-adenosylmethionine-dependent N-methyltransferase involved in the last two steps of caffeine biosynthesis, was extracted from young tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves; the CS was purified 520-fold to apparent homogeneity and a final specific activity of 5.7 nkat mg-1 protein by ammonium sulfate fractionation and hydroxyapatite, anion-exchange, adenosine-agarose, and gel-filtration chromatography. The native enzyme was monomeric with an apparent molecular mass of 61 kD as estimated by gel-filtration chromatography and 41 kD as analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The enzyme displayed a sharp pH optimum of 8.5. The final preparation exhibited 3- and 1-N-methyltransferase activity with a broad substrate specificity, showing high activity toward paraxanthine, 7-methylxanthine, and theobromine and low activity with 3-methylxanthine and 1-methylxanthine. However, the enzyme had no 7-N-methyltransferase activity toward xanthosine and xanthosine 5'-monophosphate. The Km values of CS for paraxanthine, theobromine, 7-methylxanthine, and S-adenosylmethionine were 24, 186, 344, and 21 microM, respectively. The possible role and regulation of CS in purine alkaloid biosynthesis in tea leaves are discussed. The 20-amino acid N-terminal sequence for CS showed little homology with other methyltransferases.
Figures

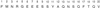
Similar articles
-
Biosynthesis of caffeine by tea-leaf extracts. Enzymic formation of theobromine from 7-methylxanthine and of caffeine from theobromine.Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):87-96. doi: 10.1042/bj1460087. Biochem J. 1975. PMID: 238504 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeine synthase and related methyltransferases in plants.Front Biosci. 2004 May 1;9:1833-42. doi: 10.2741/1364. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14977590 Review.
-
7-Methylxanthine methyltransferase of coffee plants. Gene isolation and enzymatic properties.J Biol Chem. 2001 Mar 16;276(11):8213-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009480200. Epub 2000 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11108716
-
Molecular and biochemical characterization of caffeine synthase and purine alkaloid concentration in guarana fruit.Phytochemistry. 2014 Sep;105:25-36. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.04.018. Epub 2014 May 21. Phytochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24856135
-
Biosynthesis of caffeine underlying the diversity of motif B' methyltransferase.Nat Prod Commun. 2015 May;10(5):799-801. Nat Prod Commun. 2015. PMID: 26058161 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolite and Transcriptome Profiling on Xanthine Alkaloids-Fed Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) Shoot Tips and Roots Reveal the Complex Metabolic Network for Caffeine Biosynthesis and Degradation.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Sep 9;11:551288. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.551288. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33013969 Free PMC article.
-
Dissection of Chemical Composition and Associated Gene Expression in the Pigment-Deficient Tea Cultivar 'Xiaoxueya' Reveals an Albino Phenotype and Metabolite Formation.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Nov 27;10:1543. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01543. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31827483 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor CsS40 negatively regulates TCS1 expression and caffeine biosynthesis in connection to leaf senescence in Camellia sinensis.Hortic Res. 2023 Aug 10;10(9):uhad162. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhad162. eCollection 2023 Sep. Hortic Res. 2023. PMID: 37731861 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeine biosynthesis and degradation in tea [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze] is under developmental and seasonal regulation.Mol Biotechnol. 2009 Oct;43(2):104-11. doi: 10.1007/s12033-009-9188-2. Epub 2009 May 29. Mol Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19479388
-
Regulation of miR163 and its targets in defense against Pseudomonas syringae in Arabidopsis thaliana.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 12;7:46433. doi: 10.1038/srep46433. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28401908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashihara H, Crozier A. Biosynthesis and metabolism of caffeine and related purine alkaloids in plants. In: Callow JA, editor. Advances in Botanical Research, Vol 30. London: Academic Press; 1999. pp. 117–205.
-
- Ashihara H, Gillies FM, Crozier A. Metabolism of caffeine and related purine alkaloids in leaves of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Plant Cell Physiol. 1997;38:413–419.
-
- Ashihara H, Kato M, Ye C. J Plant Res. 1998;111:599–604.
-
- Ashihara H, Kubota H. Patterns of adenine metabolism and caffeine biosynthesis in different parts of tea seedlings. Physiol Plant. 1986;68:275–281.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

