Combination therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised, controlled, double blind 52 week clinical trial of sulphasalazine and methotrexate compared with the single components
- PMID: 10364900
- PMCID: PMC1752864
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.58.4.220
Combination therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised, controlled, double blind 52 week clinical trial of sulphasalazine and methotrexate compared with the single components
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the potential clinical benefit of a combination therapy.
Methods: 205 patients fulfilling the ACR criteria for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), not treated with disease modifying antirheumatoid drugs previously, with an early (< or = 1 year duration), active (Disease Activity Score (DAS) > 3.0), rheumatoid factor and/or HLA DR 1/4 positive disease were randomised between sulphasalazine (SASP) 2000 (maximum 3000) mg daily (n = 68), or methotrexate (MTX) 7.5 (maximum 15) mg weekly (n = 69) or the combination (SASP + MTX) of both (n = 68).
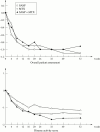
Results: The mean changes in the DAS during the one year follow up of the study was -1.15, -0.87, -1.26 in the SASP, MTX, and SASP + MTX group respectively (p = 0.019). However, there was no statistically significant difference in terms of either EULAR good responders 34%, 38%, 38% or ACR criteria responders 59%, 59%, 65% in the SASP, MTX, and SASP + MTX group respectively. Radiological progression evaluated by the modified Sharp score was very modest in the three groups: mean changes in erosion score: +2.4, +2.4, +1.9, in narrowing score: +2.3, +2.1, +1.6 and in total damage score: +4.6, +4.5, +3.5, in the SASP, MTX, and SASP + MTX groups respectively. Adverse events occurred more frequently in the SASP + MTX group 91% versus 75% in the SASP and MTX group (p = 0.025). Nausea was the most frequent side effect: 32%, 23%, 49% in the SASP, MTX, and SASP + MTX groups respectively (p = 0.007).
Conclusion: This study suggests that an early initiation therapy of disease modifying drug seems to be of benefit. However, this study was unable to demonstrate a clinically relevant superiority of the combination therapy although several outcomes were in favour of this observation. The tolerability of the three treatment modalities seems acceptable.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials