Hydroxychloroquine treatment for primary Sjögren's syndrome: its effect on salivary and serum inflammatory markers
- PMID: 10364906
- PMCID: PMC1752865
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.58.4.253
Hydroxychloroquine treatment for primary Sjögren's syndrome: its effect on salivary and serum inflammatory markers
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of hydroxychloroquine treatment on interleukin 6 (IL6), hyaluronic acid (HA), and soluble interleukin 2 receptor (sIL2R) concentrations in the saliva and serum of patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome (SS).
Methods: Fourteen SS patients treated with hydroxychloroquine 200 mg/day for 12 months were investigated in an open prospective study. Clinical parameters of efficacy and routine biochemical and haematological data to assess drug safety and tolerability were determined every three months. Salivary and serum IL6, sIL2R, and HA values were determined at study entry, 6 and 12 months, using ELISA and radiometric assays.
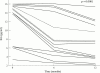
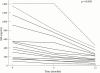
Results: After hydroxychloroquine treatment, salivary IL6 concentrations decreased from 13.2 (1.2) to 7.3 (1.1) pg/ml (mean (SEM)) (p < 0.0001). Similarly, salivary HA concentrations were also reduced from 577.8 (120) to 200 (34) ng/ml (mean (SEM) (p < 0.003). Serum IL6 concentrations decreased from 5.4 (0.6) to 2.9 (0.2) pg/ml (mean (SEM) (p < 0.001), while serum HA concentrations remained unchanged. No change has been detected in salivary or serum sIL2R concentrations after 12 months of treatment with hydroxychloroquine. Treatment also resulted in significant reduction in erythrocyte sedimentation rate, serum gamma globulin, and C reactive protein values while only partial clinical improvement was noted in some patients. A more pronounced decrease of salivary IL6 and HA levels was found in the two patients in whom a reduction in the swelling of the parotid gland was noted.
Conclusion: In this open label study of hydroxychloroquine treatment for SS a significant reduction of some salivary inflammatory markers was seen at the end of 12 months. Although during the treatment period only a partial clinical effect could be noted, the findings suggest that a double blind controlled study of hydroxychloroquine in SS is indicated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salivary and serum hyaluronic acid concentrations in patients with Sjögren's syndrome.Ann Rheum Dis. 1998 Aug;57(8):506-8. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.8.506. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998. PMID: 9797560 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary and serum interleukin 6 in primary Sjögren's syndrome.J Rheumatol. 1997 Jun;24(6):1089-91. J Rheumatol. 1997. PMID: 9195514
-
Treatment of primary Sjögren's syndrome with hydroxychloroquine: a retrospective, open-label study.Lupus. 1996 Jun;5 Suppl 1:S31-6. Lupus. 1996. PMID: 8803908 Clinical Trial.
-
Recognition and management of Sjögren's syndrome: strategies for the advanced practice nurse.Nurs Clin North Am. 2000 Mar;35(1):267-78. Nurs Clin North Am. 2000. PMID: 10673580 Review.
-
Antimalarials in Sjögren's syndrome--the Greek experience.Lupus. 1996 Jun;5 Suppl 1:S28-30. Lupus. 1996. PMID: 8803907 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of hydroxychloroquine and its metabolites in patients with connective tissue diseases.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Dec;29(6):1795-1805. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00887-8. Epub 2021 Nov 7. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34743268 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the alternative NFκB pathway improves disease symptoms in a model of Sjogren's syndrome.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028727. Epub 2011 Dec 9. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22174879 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of randomized controlled trials in the treatment of dry eye disease in Sjogren syndrome.J Inflamm (Lond). 2017 Nov 21;14:26. doi: 10.1186/s12950-017-0174-3. eCollection 2017. J Inflamm (Lond). 2017. PMID: 29200970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Metabolism: An Emerging Player in Sjögren's Syndrome.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025 Feb 11;68(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s12016-025-09023-8. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39934534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salivary gland LAMP3 mRNA expression is a possible predictive marker in the response to hydroxychloroquine in Sjögren's disease.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 23;18(2):e0282227. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282227. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36821638 Free PMC article.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials