The mdoC gene of Escherichia coli encodes a membrane protein that is required for succinylation of osmoregulated periplasmic glucans
- PMID: 10368134
- PMCID: PMC93837
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.12.3626-3631.1999
The mdoC gene of Escherichia coli encodes a membrane protein that is required for succinylation of osmoregulated periplasmic glucans
Abstract
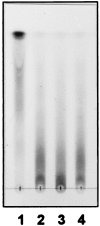
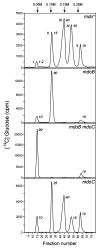
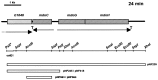
Osmoregulated periplasmic glucans (OPGs) of Escherichia coli are anionic oligosaccharides that accumulate in the periplasmic space in response to low osmolarity of the medium. Their anionic character is provided by the substitution of the glucosidic backbone by phosphoglycerol originating from the membrane phospholipids and by succinyl residues from unknown origin. A phosphoglycerol-transferase-deficient mdoB mutant was subjected to Tn5 transposon mutagenesis, and putative mutant clones were screened for changes in the anionic character of OPGs by thin-layer chromatography. One mutant deficient in succinylation of OPGs was obtained, and the gene inactivated in this mutant was characterized and named mdoC. mdoC, which encodes a membrane-bound protein, is closely linked to the mdoGH operon necessary for the synthesis of the OPG backbone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The opgGIH and opgC genes of Rhodobacter sphaeroides form an operon that controls backbone synthesis and succinylation of osmoregulated periplasmic glucans.Eur J Biochem. 2002 May;269(10):2473-84. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02907.x. Eur J Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12027885
-
Biosynthesis of osmoregulated periplasmic glucans in Escherichia coli: the membrane-bound and the soluble periplasmic phosphoglycerol transferases are encoded by the same gene.Microbiology (Reading). 2008 Feb;154(Pt 2):476-483. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/013169-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2008. PMID: 18227251
-
Identification of mdoD, an mdoG paralog which encodes a twin-arginine-dependent periplasmic protein that controls osmoregulated periplasmic glucan backbone structures.J Bacteriol. 2004 Jun;186(12):3695-702. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.12.3695-3702.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15175282 Free PMC article.
-
Osmoregulated periplasmic glucans in Proteobacteria.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000 May 1;186(1):11-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09075.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000. PMID: 10779706 Review.
-
New insights into the biological role of the osmoregulated periplasmic glucans in pathogenic and symbiotic bacteria.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2015 Oct;7(5):690-7. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12325. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26265506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The complete genome sequence and comparative genome analysis of the high pathogenicity Yersinia enterocolitica strain 8081.PLoS Genet. 2006 Dec 15;2(12):e206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020206. PLoS Genet. 2006. PMID: 17173484 Free PMC article.
-
Osmoregulated periplasmic glucans of Erwinia chrysanthemi.J Bacteriol. 2001 May;183(10):3127-33. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.10.3127-3133.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11325941 Free PMC article.
-
Osmoregulated Periplasmic Glucans.EcoSal Plus. 2017 Jun;7(2):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0001-2017. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0001-2017. EcoSal Plus. 2017. PMID: 28593831 Free PMC article.
-
The Brucella abortus cyclic beta-1,2-glucan virulence factor is substituted with O-ester-linked succinyl residues.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jul;188(14):5003-13. doi: 10.1128/JB.00086-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16816173 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Analysis of Serratia plymuthica MBSA-MJ1: A Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria That Improves Water Stress Tolerance in Greenhouse Ornamentals.Front Microbiol. 2021 May 11;12:653556. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.653556. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34046022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altabe S G, Talaga P, Wieruszeski J-M, Lippens G, Ugalde R, Bohin J-P. Periplasmic glucans of Azospirillum brasilense. In: Elmerich C, Kondorosi A, Newton W E, editors. Biological nitrogen fixation for the 21st century. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1998. p. 390.
-
- Becker A, Kleickmann A, Arnold W, Puhler A. Analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti exoH/exoK/exoLfragment: ExoK shows homology to excreted endo-β-1,3-1,4-glucanases and ExoH resembles membrane proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1993;238:145–154. - PubMed
-
- Blattner F R, Plunket III G, Bloch C A, Perna N T, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner J D, Rode C K, Mayhew G F, Gregor J, Davis N W, Kirkpatrick H A, Goeden M A, Rose D J, Mau B, Shao Y. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coliK-12. Science. 1997;277:1453–1474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

