The morphological transition of Helicobacter pylori cells from spiral to coccoid is preceded by a substantial modification of the cell wall
- PMID: 10368145
- PMCID: PMC93848
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.12.3710-3715.1999
The morphological transition of Helicobacter pylori cells from spiral to coccoid is preceded by a substantial modification of the cell wall
Abstract
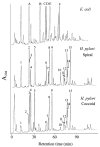
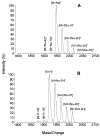
The peptidoglycan (murein) of Helicobacter pylori has been investigated by high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometric techniques. Murein from H. pylori corresponded to the A1gamma chemotype, but the muropeptide elution patterns were substantially different from the one for Escherichia coli in that the former produced high proportions of muropeptides with a pentapeptide side chain (about 60 mol%), with Gly residues as the C-terminal amino acid (5 to 10 mol%), and with (1-->6)anhydro-N-acetylmuramic acid (13 to 18 mol%). H. pylori murein also lacks murein-bound lipoprotein, trimeric muropeptides, and (L-D) cross-linked muropeptides. Cessation of growth and transition to coccoid shape triggered an increase in N-acetylglucosaminyl-N-acetylmuramyl-L-Ala-D-Glu (approximately 20 mol%), apparently at the expense of monomeric muropeptides with tri- and tetrapeptide side chains. Muropeptides with (1-->6)anhydro-muramic acid and with Gly were also more abundant in resting cells.
Figures
References
-
- Aleljung P, Nilsson H O, Wang X, Nyberg P, Morner T, Warsame I, Wadstrom T. Gastrointestinal colonisation of BALB/cA mice by Helicobacter pylorimonitored by heparin magnetic separation. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1996;13:303–309. - PubMed
-
- Blaser M J. Helicobacter pyloriand the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation. J Infect Dis. 1990;161:626–633. - PubMed
-
- Braun V, Wu H C. Lipoproteins, structure, function, biosynthesis and model for protein export. In: Ghuysen J M, Hakenbeck R, editors. Bacterial cell wall. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier Science Publisher; 1994. pp. 319–341.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

