Role of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein in limiting brain accumulation and sedative side-effects of asimadoline, a peripherally acting analgaesic drug
- PMID: 10369454
- PMCID: PMC1565984
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702497
Role of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein in limiting brain accumulation and sedative side-effects of asimadoline, a peripherally acting analgaesic drug
Abstract
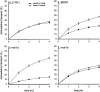
Studies with knockout mice lacking mdr1a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) have previously shown that blood-brain barrier P-gp is important in preventing the accumulation of several drugs in the brain. Asimadoline (EMD 61753) is a peripherally selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist which is under development as a therapeutic analgaesic. From the structural characteristics of this drug and its peripheral selectivity, we hypothesized that it is transported by P-gp. Using a pig-kidney polarized epithelial cell line transfected with mdr cDNAs, we demonstrate that asimadoline is transported by the mouse mdr1a P-gp and the human MDR1 P-gp. Furthermore, we show that in mdr1a/1b double knockout mice, the absence of P-gp leads to a 9 fold increased accumulation of asimadoline in the brain. In line with this accumulation difference, mdr1a/1b (-/-) mice are at least 8 fold more sensitive to the sedative effect of asimadoline than wild-type mice. Interestingly, the oral uptake of asimadoline was not substantially altered in mdr1a/1b (-/-) mice. Our results demonstrate that for some drugs, P-gp in the blood-brain barrier can have a therapeutically beneficial effect by limiting brain penetration, whereas at the same time intestinal P-gp is not a significant impediment to oral uptake of the drug.
Figures

References
-
- BORST P., SCHINKEL A.H. Genetic dissection of the function of mammalian P-glycoproteins. Trends Genet. 1997;13:217–222. - PubMed
-
- CHEN C., CHIN J.E., UEDA K., CLARK D.P., PASTAN I., GOTTESMAN M.M., RONINSON I.B. Internal duplication and homology with bacterial transport proteins in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene from multidrug-resistant human cells. Cell. 1986;47:381–389. - PubMed
-
- DRION N., LEMAIRE M., LEFAUCONNIER J.M., SCHERRMANN J.M. Role of P-glycoprotein in the blood-brain transport of colchicine and vinblastine. J. Neurochem. 1996;67:1688–1693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

