Effects of terbutaline on force and intracellular calcium in slow-twitch skeletal muscle fibres of the rat
- PMID: 10372813
- PMCID: PMC1565959
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702482
Effects of terbutaline on force and intracellular calcium in slow-twitch skeletal muscle fibres of the rat
Abstract
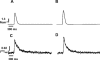
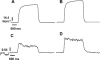
1. The effect of the alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist, terbutaline, was investigated on simultaneously measured force and intracellular free calcium ([Ca2+]i) in intact rat soleus muscle fibres, and on contractile protein function and Ca2+ content of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) in skinned fibres. 2. Terbutaline (10 microM) had no significant effect on either resting force or [Ca2+]i. Exposure to terbutaline increased both the integral of the indo-1 ratio transient and peak twitch force by 37%. 3. At sub-maximal (10 Hz) stimulation frequencies, terbutaline accelerated force relaxation but had highly variable effects on tetanic force amplitude. The corresponding indo-1 ratio transients were significantly larger, and faster to decay than the controls. 4. Terbutaline increased tetanic force at near maximal stimulation frequencies (50 Hz) by increasing tetanic [Ca2+]i. Force relaxation was accelerated at this frequency with no significant change in the indo-1 ratio transient decay rate. 5. All of terbutaline's effects on force and indo-1 ratio transients in intact fibres were completely blocked and reversed by ICI 118551 (1 microM). 6. Mechanically skinned fibres isolated from intact muscles pre-treated with terbutaline showed no significant changes in SR Ca2+ content, myofilament [Ca2+]i-sensitivity or maximum force generating capacity. 7. The results suggest that terbutaline primarily modulates force by altering the amplitude and decay rate of the [Ca2+]i transient via phosphorylation of both the ryanodine receptor (RR) and the SR pump regulatory protein, phospholamban (PLB). The high variability of responses of slow-twitch muscles to beta2-agonists probably reflects individual differences in basal phosphorylation levels of PLB relative to that of RR.
Figures



Similar articles
-
β-Adrenergic modulation of skeletal muscle contraction: key role of excitation-contraction coupling.J Physiol. 2015 Nov 1;593(21):4713-27. doi: 10.1113/JP270909. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26400207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of ADP on slow-twitch muscle fibres of the rat: implications for muscle fatigue.J Physiol. 2006 May 15;573(Pt 1):187-98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.105775. Epub 2006 Mar 23. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16556653 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of beta-adrenoceptor activation on contraction in isolated fast- and slow-twitch skeletal muscle fibres of the rat.Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):1133-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13932.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 8298802 Free PMC article.
-
Matching of sarcoplasmic reticulum and contractile properties in rat fast- and slow-twitch muscle fibres.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006 Jul;33(7):591-600. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2006.04412.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16789925
-
"Current" advances in mechanically skinned skeletal muscle fibres.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001 Aug;28(8):668-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2001.03502.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11473535 Review.
Cited by
-
Stress-induced increase in skeletal muscle force requires protein kinase A phosphorylation of the ryanodine receptor.J Physiol. 2012 Dec 15;590(24):6381-7. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.237925. Epub 2012 Oct 15. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23070698 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of sympathetic nervous system on sensorimotor function: whiplash associated disorders (WAD) as a model.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006 Nov;98(5):423-49. doi: 10.1007/s00421-006-0312-8. Epub 2006 Oct 12. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006. PMID: 17036216 Review.
-
A multiplexed in vitro assay system for evaluating human skeletal muscle functionality in response to drug treatment.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020 Mar;117(3):736-747. doi: 10.1002/bit.27231. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020. PMID: 31758543 Free PMC article.
-
β-Adrenergic modulation of skeletal muscle contraction: key role of excitation-contraction coupling.J Physiol. 2015 Nov 1;593(21):4713-27. doi: 10.1113/JP270909. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26400207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional β-adrenoceptors are important for early muscle regeneration in mice through effects on myoblast proliferation and differentiation.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 7;9(7):e101379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101379. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25000590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BOWMAN W.C. Effects of adrenergic activators and inhibitors on the skeletal muscles. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 1980.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

