Role of the medial prefrontal cortex in 5-HT1A receptor-induced inhibition of 5-HT neuronal activity in the rat
- PMID: 10372816
- PMCID: PMC1565963
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702510
Role of the medial prefrontal cortex in 5-HT1A receptor-induced inhibition of 5-HT neuronal activity in the rat
Abstract
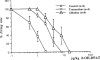
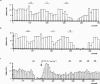
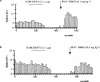
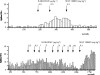
1. We examined the involvement of the frontal cortex in the 5-HT2A receptor-induced inhibition of 5-HT neurones in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) of the anaesthetized rat using single-unit recordings complemented by Fos-immunocytochemistry. 2. Both transection of the frontal cortex as well as ablation of the medial region of the prefrontal cortex (mPFC) significantly attenuated the inhibition of 5-HT neurones induced by systemic administration of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist, 8-OH-DPAT (0.5-16 microg kg(-1), i.v.). In comparison, the response to 8-OH-DPAT was not altered by ablation of the parietal cortex. The inhibitory effect of 8-OH-DPAT was reversed by the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, WAY 100635 (0.1 mg kg(-1), i.v.) in all neurones tested. 3. In contrast, cortical transection did not alter the sensitivity of 5-HT neurones to iontophoretic application of 8-OH-DPAT into the DRN. Similarly, cortical transection did not alter the sensitivity of 5-HT neurones to systemic administration of the selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitor, paroxetine (0.1-0.8 mg kg(-1) , i.v.). 4. 8-OH-DPAT evoked excitation of mPFC neurones at doses (0.5-32 microg kg(-1), i.v.) in the range of those which inhibited 5-HT cell firing. At higher doses (32-512 microg kg(-1), i.v.) 8-OH-DPAT inhibited mPFC neurones. 8-OH-DPAT (0.1 mg kg(-1), s.c.) also induced Fos expression in the mPFC. The neuronal excitation and inhibition, as well as the Fos expression, were antagonized by WAY 100635. 5. These data add further support to the view that the inhibitory effect of 5-HT1A receptor agonists on the firing activity of DRN 5-HT neurones involves, in part, activation of a 5-HT1A receptor-mediated postsynaptic feedback loop centred on the mPFC.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Control of dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons by the medial prefrontal cortex: Involvement of serotonin-1A, GABA(A), and glutamate receptors.J Neurosci. 2001 Dec 15;21(24):9917-29. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-24-09917.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11739599 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo inhibition of neuronal activity in the rat ventromedial prefrontal cortex by midbrain-raphe nuclei: role of 5-HT1A receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2003 Jul;45(1):72-81. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(03)00139-4. Neuropharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12814660
-
Effects of 5-HT and 5-HT1A receptor agonists and antagonists on dorsal vagal preganglionic neurones in anaesthetized rats: an ionophoretic study.Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Oct;116(4):2291-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15067.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8564262 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of (+)- and (-)-8- and 7-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin at human (h)D3, hD2 and h serotonin1A receptors and their modulation of the activity of serotoninergic and dopaminergic neurones in rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Mar;280(3):1241-9. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997. PMID: 9067310
-
A pharmacological analysis of an associative learning task: 5-HT(1) to 5-HT(7) receptor subtypes function on a pavlovian/instrumental autoshaped memory.Learn Mem. 2003 Sep-Oct;10(5):363-72. doi: 10.1101/lm.60503. Learn Mem. 2003. PMID: 14557609 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of anxiety by cortical serotonin 1A receptors.Front Behav Neurosci. 2015 Feb 24;9:48. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00048. eCollection 2015. Front Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25759645 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal Nicotine Reduces Chemosensitivity of Medullary 5-HT Neurons after Maturation in Culture.Neuroscience. 2020 Oct 15;446:80-93. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.08.012. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Neuroscience. 2020. PMID: 32818601 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptors trigger neurosecretion of 5-HT within dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat in the absence of action potential firing.J Physiol. 2006 Dec 15;577(Pt 3):891-905. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.115311. Epub 2006 Oct 19. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 17053037 Free PMC article.
-
Flibanserin, a drug intended for treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder in pre-menopausal women, affects spontaneous motor activity and brain neurochemistry in female rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;381(6):573-9. doi: 10.1007/s00210-010-0515-8. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20422156
-
Control of dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons by the medial prefrontal cortex: Involvement of serotonin-1A, GABA(A), and glutamate receptors.J Neurosci. 2001 Dec 15;21(24):9917-29. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-24-09917.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11739599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AGHAJANIAN G.K.Feedback regulation of central monoaminergic neurons: Evidence from single cell recording studies Essays in Neurochemistry and Neuropharmacology 19783Chichester: John Wiley & Sons; 2–32.ed Youdim, M.B.H., Lovenberg, W., Sharman, D.F. & Lagnado, J.R.Volume - PubMed
-
- AGHAJANIAN G.K., HAIGLER H.J., BLOOM F.E. Lysergic acid diethylamide and serotonin: direct action on serotonin-containing neurons in rat brain. Life. Sci. 1972;11:615–622. - PubMed
-
- AGHAJANIAN G.K., LAKOSKI J.M. Hyperpolarization of serotonergic neurones by serotonin and LSD: studies in brain slices showing increased K+ conductance. Brain Res. 1984;305:181–185. - PubMed
-
- AGHAJANIAN G.K., WANG R.Y., BARABAN J. Serotonergic and non-serotonergic neurons of the dorsal raphe: reciprocal changes in firing induced by peripheral nerve stimulation. Brain Res. 1978;153:169–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

