Direct inhibition of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel by dopamine and (+)-SKF38393
- PMID: 10372829
- PMCID: PMC1565957
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702479
Direct inhibition of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel by dopamine and (+)-SKF38393
Abstract
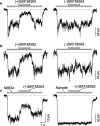
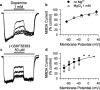
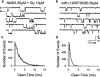
1. Dopamine is known to modulate glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the retina and in several brain regions by activating specific G-protein-coupled receptors. We have examined the possibility of a different type of mechanism for this modulation, one involving direct interaction of dopamine with ionotropic glutamate receptors. 2. Ionic currents induced by fast application of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) were recorded under whole-cell patch-clamp in cultured striatal, thalamic and hippocampal neurons of the rat and in retinal neurons of the chick. Dopamine at concentrations above 100 microM inhibited the NMDA response in all four neuron types, exhibiting an IC50 of 1.2 mM in hippocampal neurons. The time course of this inhibition was fast, developing in less than 100 ms. 3. The D1 receptor agonist (+)-SKF38393 mimicked the effect of dopamine, with an IC50 of 58.9 microM on the NMDA response, while the enantiomer (-)-SKF38393 was ineffective at 50 microM. However, the D1 antagonist R(+)-SCH23390 did not prevent the inhibitory effect of (+)-SKF38393. 4. The degree of inhibition by dopamine and (+)-SKF38393 depended on transmembrane voltage, increasing 2.7 times with a hyperpolarization of about 80 mV. The voltage-dependent block by dopamine was also observed in the presence of MgCl2 1 mM. 5. Single-channel recordings showed that the open times of NMDA-gated channels were shortened by (+)-SKF38393. 6. These data suggested that the site to which the drugs bound to produce the inhibitory effect was distinct from the classical D1-type dopamine receptor sites, possibly being located inside the NMDA channel pore. It is concluded that dopamine and (+)-SKF38393 are NMDA channel ligands.
Figures


References
-
- AKAIKE A., OHNO Y., SASA M., TAKAORI S. Excitatory and inhibitory effects of dopamine on neuronal activity of the caudate nucleus neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1987;418:262–272. - PubMed
-
- ALKONDON M., ALBUQUERQUE E.X. Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. I. Pharmacological and functional evidence for distinct structural subtypes. J. Pharmacol. Exper. Therap. 1993;265:1455–1473. - PubMed
-
- ANDERSEN P.H., JANSEN J.A. Dopamine receptor agonists: selectivity and dopamine D1 receptor efficacy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1990;188:335–347. - PubMed
-
- BRAUN A., FABBRINI G., MOURADIAN M.M., SERRATI C., BARONE P., CHASE T.N. Selective D-1 dopamine receptor agonist treatment of Parkinson's disease. J. Neural Transm. 1987;68:41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

