Dominant negative murine serum response factor: alternative splicing within the activation domain inhibits transactivation of serum response factor binding targets
- PMID: 10373507
- PMCID: PMC84256
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.4582
Dominant negative murine serum response factor: alternative splicing within the activation domain inhibits transactivation of serum response factor binding targets
Abstract
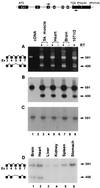
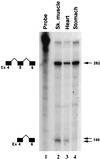
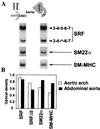
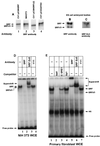
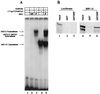
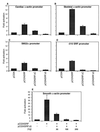
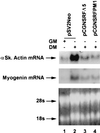
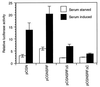
Primary transcripts encoding the MADS box superfamily of proteins, such as MEF2 in animals and ZEMa in plants, are alternatively spliced, producing several isoformic species. We show here that murine serum response factor (SRF) primary RNA transcripts are alternatively spliced at the fifth exon, deleting approximately one-third of the C-terminal activation domain. Among the different muscle types examined, visceral smooth muscles have a very low ratio of SRFDelta5 to SRF. Increased levels of SRFDelta5 correlates well with reduced smooth muscle contractile gene activity within the elastic aortic arch, suggesting important biological roles for differential expression of SRFDelta5 variant relative to wild-type SRF. SRFDelta5 forms DNA binding-competent homodimers and heterodimers. SRFDelta5 acts as a naturally occurring dominant negative regulatory mutant that blocks SRF-dependent skeletal alpha-actin, cardiac alpha-actin, smooth alpha-actin, SM22alpha, and SRF promoter-luciferase reporter activities. Expression of SRFDelta5 interferes with differentiation of myogenic C2C12 cells and the appearance of skeletal alpha-actin and myogenin mRNAs. SRFDelta5 repressed the serum-induced activity of the c-fos serum response element. SRFDelta5 fused to the yeast Gal4 DNA binding domain displayed low transcriptional activity, which was complemented by overexpression of the coactivator ATF6. These results indicate that the absence of exon 5 might be bypassed through recruitment of transcription factors that interact with extra-exon 5 regions in the transcriptional activating domain. The novel alternatively spliced isoform of SRF, SRFDelta5, may play an important regulatory role in modulating SRF-dependent gene expression.
Figures
References
-
- Belaguli N S, Schildmeyer L A, Schwartz R J. Organization and myogenic restricted expression of the murine serum response factor gene. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:18222–18231. - PubMed
-
- Belaguli, N. S., J. L. Sepulveda, V. Nigam, and R. J. Schwartz. Unpublished data.
-
- Bickmore W A, Oghene K, Little M H, Seawright A, VanHeyningen V, Hastie N D. Modulation of DNA binding specificity by alternative splicing of the Wilms tumor wt1 gene transcript. Science. 1992;257:235–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
