Mutant cells that do not respond to interleukin-1 (IL-1) reveal a novel role for IL-1 receptor-associated kinase
- PMID: 10373513
- PMCID: PMC84262
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.4643
Mutant cells that do not respond to interleukin-1 (IL-1) reveal a novel role for IL-1 receptor-associated kinase
Abstract
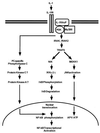
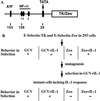
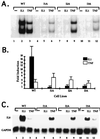
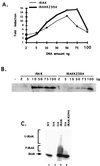
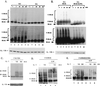
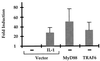
Mutagenized human 293 cells containing an interleukin-1 (IL-1)-regulated herpes thymidine kinase gene, selected in IL-1 and gancyclovir, have yielded many independent clones that are unresponsive to IL-1. The four clones analyzed here carry recessive mutations and represent three complementation groups. Mutant A in complementation group I1 lacks IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK), while the mutants in the other two groups are defective in unknown components that function upstream of IRAK. Expression of exogenous IRAK in I1A cells (I1A-IRAK) restores their responsiveness to IL-1. Neither NFkappaB nor Jun kinase is activated in IL-1-treated I1A cells, but these responses are restored in I1A-IRAK cells, indicating that IRAK is required for both. To address the role of the kinase activity of IRAK in IL-1 signaling, its ATP binding site was mutated (K239A), completely abolishing kinase activity. In transfected I1A cells, IRAK-K239A was still phosphorylated upon IL-1 stimulation and, surprisingly, still complemented all the defects in the mutant cells. Therefore, IRAK must be phosphorylated by a different kinase, and phospho-IRAK must play a role in IL-1-mediated signaling that does not require its kinase activity.
Figures

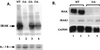

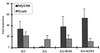

Similar articles
-
IRAK4 kinase activity is redundant for interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase phosphorylation and IL-1 responsiveness.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jun 18;279(25):26748-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400785200. Epub 2004 Apr 14. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15084582
-
Effects of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) expression on IL-1 signaling are independent of its kinase activity.FEBS Lett. 1999 Apr 1;448(1):81-5. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00322-1. FEBS Lett. 1999. PMID: 10217414
-
IRAK and TAK1 are required for IL-18-mediated signaling.Eur J Immunol. 2001 Dec;31(12):3747-54. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200112)31:12<3747::aid-immu3747>3.0.co;2-e. Eur J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11745395
-
Functional diversity and regulation of different interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family members.Mol Cell. 2003 Feb;11(2):293-302. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00053-4. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12620219 Review.
-
The interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases: critical regulators of innate immune signalling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Dec 15;80(12):1981-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.020. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20599782 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Inhibition of Rip2 and IRAK1/4 Regulates IL-1β and IL-6 in Sarcoidosis Alveolar Macrophages and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells.J Immunol. 2016 Aug 15;197(4):1368-78. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600258. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27402699 Free PMC article.
-
CD26 mediates dissociation of Tollip and IRAK-1 from caveolin-1 and induces upregulation of CD86 on antigen-presenting cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Sep;25(17):7743-57. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.17.7743-7757.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16107720 Free PMC article.
-
Mutagenesis by reversible promoter insertion to study the activation of NF-kappaB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 3;102(18):6425-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502463102. Epub 2005 Apr 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15851657 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant human cells with constitutive activation of NF-kappaB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 6;101(1):192-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0306812101. Epub 2003 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14691254 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1) as a therapeutic strategy.Oncotarget. 2018 Sep 7;9(70):33416-33439. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26058. eCollection 2018 Sep 7. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30279971 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adachi O, Kawai T, Takeda K, Matsumoto M, Tsutsui H, Sakagami M, Nakanishi K, Akira S. Targeted disruption of the MyD88 gene results in loss of IL-1 and IL-18-mediated function. Immunity. 1998;9:143–150. - PubMed
-
- Aizawa S, Nakano H, Ishida T, Horie R, Nagai M, Ito K, Yagita H, Okumura K, Inoue J, Watanabe T. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 5 and TRAF2 are involved in CD30-mediated NFκB activation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:2042–2045. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P A, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P A, Henkel T. Function and activation of NFκB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
