Induction of apoptosis by double-stranded-RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) involves the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 and NF-kappaB
- PMID: 10373514
- PMCID: PMC84263
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.4653
Induction of apoptosis by double-stranded-RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) involves the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 and NF-kappaB
Abstract
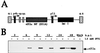
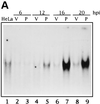
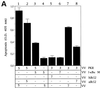
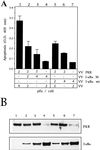
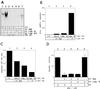
The double-stranded (ds) RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) is a key mediator of antiviral effects of interferon (IFN) and an active player in apoptosis induced by different stimuli. The translation initiation factor eIF-2alpha (alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2) and IkappaBalpha, the inhibitor of the transcription factor NF-kappaB, have been proposed as downstream mediators of PKR effects. To evaluate the involvement of NF-kappaB and eIF-2alpha in the induction of apoptosis by PKR, we have used vaccinia virus (VV) recombinants that inducibly express PKR concomitantly with a dominant negative mutant of eIF-2alpha or a repressor form of IkappaBalpha. We found that while expression of PKR by a VV vector resulted in extensive inhibition of protein synthesis and induction of apoptosis, coexpression of PKR with a dominant negative mutant of eIF-2alpha (Ser-51-->Ala) reversed both the PKR-mediated translational block and PKR-induced apoptosis. Coexpression of PKR with a repressor form of IkappaBalpha (Ser-32, 36-Ala) also leads to the inhibition of apoptosis by abolishing NF-kappaB induction, while translation remains blocked. Treating cells with two different proteasome inhibitors which block IkappaBalpha degradation, prevented PKR-induced apoptosis, supporting results from coexpression studies. Biochemical analysis and transient assays revealed that PKR expression by a VV vector induced NF-kappaB binding and transactivation. In addition, upregulation of Fas mRNA transcription occurred during PKR activation. Our findings provide direct evidence for the involvement of eIF-2alpha and NF-kappaB in the induction of apoptosis by PKR.
Figures




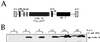


References
-
- Abbaddie C N, Kabrun F, Bouali F, Vandenbunder B, Enrietto P. High levels of c-rel expression are associated with programmed cell death in the developing avian embryo and in bone marrow cells in vitro. Cell. 1993;75:899–912. - PubMed
-
- Alcamí J, Lain de Lera T, Folgueira L, Pedraza M A, Jacqué J M, Bachelerie F, Noriega A R, Hay R T, Harrich D, Gaynor R B, Virelizier J L, Arenzana-Seisdedos F. Absolute dependence on κB responsive elements for initiation and Tat-mediated amplification of HIV transcription in blood CD4 T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1995;14:1552–1560. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P A, Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
