Osmotic shock inhibits insulin signaling by maintaining Akt/protein kinase B in an inactive dephosphorylated state
- PMID: 10373517
- PMCID: PMC84266
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.4684
Osmotic shock inhibits insulin signaling by maintaining Akt/protein kinase B in an inactive dephosphorylated state
Abstract
We have previously reported that insulin and osmotic shock stimulate an increase in glucose transport activity and translocation of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter isoform GLUT4 to the plasma membrane through distinct pathways in 3T3L1 adipocytes (D. Chen, J. S. Elmendorf, A. L. Olson, X. Li, H. S. Earp, and J. E. Pessin, J. Biol. Chem. 272:27401-27410, 1997). In investigations of the relationships between these two signaling pathways, we have now observed that these two stimuli are not additive, and, in fact, osmotic shock pretreatment was found to completely prevent any further insulin stimulation of glucose transport activity and GLUT4 protein translocation. In addition, osmotic shock inhibited the insulin stimulation of lipogenesis and glycogen synthesis. This inhibition of insulin-stimulated downstream signaling occurred without any significant effect on insulin receptor autophosphorylation or tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1). Furthermore, there was no effect on either the insulin-stimulated association of the p85 type I phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase regulatory subunit with IRS1 or phosphotyrosine antibody-immunoprecipitated PI 3-kinase activity. In contrast, osmotic shock pretreatment markedly inhibited the insulin stimulation of protein kinase B (PKB) and p70S6 kinase activities. In addition, the dephosphorylation of PKB was prevented by pretreatment with the phosphatase inhibitors okadaic acid and calyculin A. These data support a model in which osmotic shock-induced insulin resistance of downstream biological responses results from an inhibition of insulin-stimulated PKB activation.
Figures


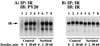
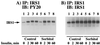






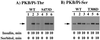
Similar articles
-
Calmodulin antagonists inhibit insulin-stimulated GLUT4 (glucose transporter 4) translocation by preventing the formation of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in 3T3L1 adipocytes.Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Feb;14(2):317-26. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.2.0425. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10674403
-
Hydrogen peroxide generated during cellular insulin stimulation is integral to activation of the distal insulin signaling cascade in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2001 Dec 28;276(52):48662-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105061200. Epub 2001 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11598110
-
Engagement of the insulin-sensitive pathway in the stimulation of glucose transport by alpha-lipoic acid in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Diabetologia. 2000 Mar;43(3):294-303. doi: 10.1007/s001250050047. Diabetologia. 2000. PMID: 10768090
-
Insulin signaling and the regulation of glucose transport.Mol Med. 2004 Jul-Dec;10(7-12):65-71. doi: 10.2119/2005-00029.Saltiel. Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 16307172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-Responsive Transcription Factors.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 15;11(12):1886. doi: 10.3390/biom11121886. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944530 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The TORC1-activated Proteins, p70S6K and GRB10, Regulate IL-4 Signaling and M2 Macrophage Polarization by Modulating Phosphorylation of Insulin Receptor Substrate-2.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 25;291(48):24922-24930. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.756791. Epub 2016 Oct 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27742835 Free PMC article.
-
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-1, 3-acetate induces the negative regulation of protein kinase B by protein kinase Calpha during gastric cancer cell apoptosis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2010 Sep;15(3):377-94. doi: 10.2478/s11658-010-0014-4. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20428959 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the activity of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase by Akt in cancer and adenoviral protein E1A-mediated sensitization to apoptosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Oct;23(19):6836-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.19.6836-6848.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12972603 Free PMC article.
-
Intramolecular and intermolecular interactions of protein kinase B define its activation in vivo.PLoS Biol. 2007 Apr;5(4):e95. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050095. PLoS Biol. 2007. PMID: 17407381 Free PMC article.
-
Nelfinavir-induced insulin resistance is associated with impaired plasma membrane recruitment of the PI 3-kinase effectors Akt/PKB and PKC-zeta.Diabetologia. 2004 Jun;47(6):1107-17. doi: 10.1007/s00125-004-1408-5. Epub 2004 May 28. Diabetologia. 2004. PMID: 15168016
References
-
- Alessi D R, Cohen P. Mechanism of activation and function of protein kinase B. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998;8:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Alessi D R, Deak M, Casamayor A, Caudwell F B, Morrice N, Norman D G, Gaffney P, Reese C B, MacDougall C N, Harbison D, Ashworth A, Bownes M. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1): structural and functional homology with the Drosophila DSTPK61 kinase. Curr Biol. 1997;7:776–789. - PubMed
-
- Alessi D R, James S R, Downes C P, Holmes A B, Gaffney P R, Reese C B, Cohen P. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase B alpha. Curr Biol. 1997;7:261–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
