SDF-2 induction of terminal differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum is mediated by the membrane-spanning sensor kinase DhkA
- PMID: 10373524
- PMCID: PMC84273
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.4750
SDF-2 induction of terminal differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum is mediated by the membrane-spanning sensor kinase DhkA
Abstract
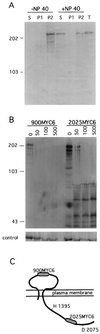
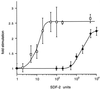
SDF-2 is a peptide released by prestalk cells during culmination that stimulates prespore cells to encapsulate. Genetic evidence indicates that the response is dependent on the dhkA gene. This gene encodes a member of the histidine kinase family of genes that functions in two-component signal transduction pathways. The sequence of the N-terminal half of DhkA predicts two hydrophobic domains separated by a 310-amino-acid loop that could bind a ligand. By inserting MYC6 epitopes into DhkA, we were able to show that the loop is extracellular while the catalytic domain is cytoplasmic. Cells expressing the MYC epitope in the extracellular domain of DhkA were found to respond only if induced with 100-fold-higher levels of SDF-2 than required to induce dhkA+ cells; however, they could be induced to sporulate by addition of antibodies specific to the MYC epitope. To examine the enzymatic activity of DhkA, we purified the catalytic domain following expression in bacteria and observed incorporation of labelled phosphate from ATP consistent with histidine autophosphorylation. Site-directed mutagenesis of histidine1395 to glutamine in the catalytic domain blocked autophosphorylation. Furthermore, genetic analyses showed that histidine1395 and the relay aspartate2075 of DhkA are both critical to its function but that another histidine kinase, DhkB, can partially compensate for the lack of DhkA activity. Sporulation is drastically reduced in double mutants lacking both DhkA and DhkB. Suppressor studies indicate that the cyclic AMP (cAMP) phosphodiesterase RegA and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase PKA act downstream of DhkA.
Figures


References
-
- Abe H, Uchiyama M, Tanaka Y, Saito H. Structure of discadenine, a spore germination inhibitor from the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1976;42:3807–3810.
-
- Abe K, Yanagisawa K. A new class of rapid developing mutants in Dictyostelium discoideum: implications for cyclic AMP metabolism and cell differentiation. Dev Biol. 1983;95:200–210. - PubMed
-
- Alex L, Simon M. Protein histidine kinases and signal transduction in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1994;10:133–138. - PubMed
-
- Anjard C, Pinaud S, Kay R R, Reymond C D. Overexpression of DdPK2 protein kinase causes rapid development and affects the intracellular cAMP pathway of Dictyostelium discoideum. Development. 1992;115:785–790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
