Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in response to interleukin-1 leads to phosphorylation and activation of the NF-kappaB p65/RelA subunit
- PMID: 10373529
- PMCID: PMC84278
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.4798
Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in response to interleukin-1 leads to phosphorylation and activation of the NF-kappaB p65/RelA subunit
Abstract
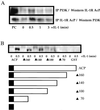
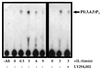
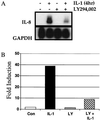
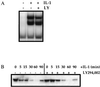
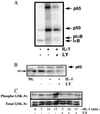
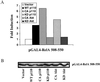
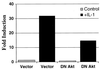
The work of Reddy et al. (S. A. Reddy, J. A. Huang, and W. S. Liao, J. Biol. Chem. 272:29167-29173, 1997) reveals that phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) plays a role in transducing a signal from the occupied interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor to nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB), but the underlying mechanism remains to be determined. We have found that IL-1 stimulates interaction of the IL-1 receptor accessory protein with the p85 regulatory subunit of PI3K, leading to the activation of the p110 catalytic subunit. Specific PI3K inhibitors strongly inhibit both PI3K activation and NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression but have no effect on the IL-1-stimulated degradation of IkappaBalpha, the nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB, or the ability of NF-kappaB to bind to DNA. In contrast, PI3K inhibitors block the IL-1-stimulated phosphorylation of NF-kappaB itself, especially the p65/RelA subunit. Furthermore, by using a fusion protein containing the p65/RelA transactivation domain, we found that overexpression of the p110 catalytic subunit of PI3K induces p65/RelA-mediated transactivation and that the specific PI3K inhibitor LY294,002 represses this process. Additionally, the expression of a constitutively activated form of either p110 or the PI3K-activated protein kinase Akt also induces p65/RelA-mediated transactivation. Therefore, IL-1 stimulates the PI3K-dependent phosphorylation and transactivation of NF-kappaB, a process quite distinct from the liberation of NF-kappaB from its cytoplasmic inhibitor IkappaB.
Figures

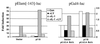
Similar articles
-
Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 Subunit of NF-kappa B through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 1;276(22):18934-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101103200. Epub 2001 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11259436
-
Requirement for both JAK-mediated PI3K signaling and ACT1/TRAF6/TAK1-dependent NF-kappaB activation by IL-17A in enhancing cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells.J Immunol. 2007 Nov 15;179(10):6504-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.6504. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17982039
-
Prostaglandin E2 induces interleukin-6 expression in human chondrocytes via cAMP/protein kinase A- and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent NF-kappaB activation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Jun;298(6):C1445-56. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00508.2009. Epub 2010 Mar 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20457835 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting NF-κB activation by small molecules as a therapeutic strategy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Oct-Dec;1799(10-12):775-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.05.004. Epub 2010 May 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20493977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TLR-4, IL-1R and TNF-R signaling to NF-kappaB: variations on a common theme.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Oct;65(19):2964-78. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8064-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18535784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal lipids induce human pancreatic tumoral MiaPaCa-2 cells resistance through the CXCR4-SDF-1α signaling axis.Oncoscience. 2014 Nov 11;2(1):15-30. doi: 10.18632/oncoscience.96. eCollection 2015. Oncoscience. 2014. PMID: 25821841 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in RAW264.7 macrophages of malvidin, a major red wine polyphenol.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 5;8(6):e65355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065355. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23755222 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and genetic accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha enhances excitatory synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons through the production of vascular endothelial growth factor.J Neurosci. 2010 Apr 28;30(17):6080-93. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5493-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20427666 Free PMC article.
-
Heterophyllin B Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in RAW 264.7 Macrophages by Suppressing the PI3K/Akt Pathways.Molecules. 2018 Mar 21;23(4):717. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040717. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29561811 Free PMC article.
-
Trinity of inflammation, innate immune cells and cross-talk of signalling pathways in tumour microenvironment.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 17;14:1255727. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1255727. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37680708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baeuerle P A, Henkel T. Function and activation of NF κB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
-
- Barnes P J, Karin M. Nuclear factor-κB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1066–1071. - PubMed
-
- Basu S, Rosenzweig K R, Youmell M, Price B D. The DNA-dependent protein kinase participates in the activation of NFκB following DNA damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;247:79–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
