Induced focal adhesion kinase (FAK) expression in FAK-null cells enhances cell spreading and migration requiring both auto- and activation loop phosphorylation sites and inhibits adhesion-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Pyk2
- PMID: 10373530
- PMCID: PMC84279
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.4806
Induced focal adhesion kinase (FAK) expression in FAK-null cells enhances cell spreading and migration requiring both auto- and activation loop phosphorylation sites and inhibits adhesion-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Pyk2
Abstract
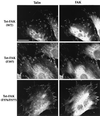
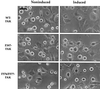
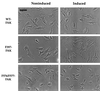
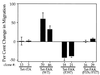
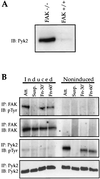
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinase involved in integrin-mediated control of cell behavior. Following cell adhesion to components of the extracellular matrix, FAK becomes phosphorylated at multiple sites, including tyrosines 397, 576, and 577. Tyr-397 is an autophosphorylation site that promotes interaction with c-Src or Fyn. Tyr-576 and Tyr-577 lie in the putative activation loop of the kinase domain, and FAK catalytic activity may be elevated through phosphorylation of these residues by associated Src family kinase. Recent studies have implicated FAK as a positive regulator of cell spreading and migration. To further study the mechanism of adhesion-induced FAK activation and the possible role and signaling requirements for FAK in cell spreading and migration, we utilized the tetracycline repression system to achieve inducible expression of either wild-type FAK or phosphorylation site mutants in fibroblasts derived from FAK-null mouse embryos. Using these Tet-FAK cells, we demonstrated that both the FAK autophosphorylation and activation loop sites are critical for maximum adhesion-induced FAK activation and FAK-enhanced cell spreading and migration responses. Negative effects on cell spreading and migration, as well as decreased phosphorylation of the substrate p130(Cas), were observed upon induced expression of the FAK autophosphorylation site mutant. These negative effects appear to result from an inhibition of integrin-mediated signaling by the FAK-related kinase Pyk2/CAKbeta/RAFTK/CadTK.
Figures


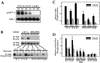

Similar articles
-
Multiple Grb2-mediated integrin-stimulated signaling pathways to ERK2/mitogen-activated protein kinase: summation of both c-Src- and focal adhesion kinase-initiated tyrosine phosphorylation events.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 May;18(5):2571-85. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.5.2571. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9566877 Free PMC article.
-
Pyk2 and Src-family protein-tyrosine kinases compensate for the loss of FAK in fibronectin-stimulated signaling events but Pyk2 does not fully function to enhance FAK- cell migration.EMBO J. 1998 Oct 15;17(20):5933-47. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.20.5933. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9774338 Free PMC article.
-
Different modes and qualities of tyrosine phosphorylation of Fak and Pyk2 during epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation and cell migration: analysis of specific phosphorylation events using site-directed antibodies.Oncogene. 2001 May 10;20(21):2626-35. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204359. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11420674
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin, FAK, and p130CAS: effects on cell spreading and migration.Front Biosci. 2002 Jan 1;7:d143-50. doi: 10.2741/A771. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 11779709 Review.
-
Focal adhesion kinase in integrin-mediated signaling.Front Biosci. 1999 Jan 15;4:D102-13. doi: 10.2741/cary. Front Biosci. 1999. PMID: 9889179 Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating extracellular vesicles from patients with breast cancer enhance migration and invasion via a Src‑dependent pathway in MDA‑MB‑231 breast cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Sep;22(3):1932-1948. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11259. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32582965 Free PMC article.
-
R-Ras promotes focal adhesion formation through focal adhesion kinase and p130(Cas) by a novel mechanism that differs from integrins.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Feb;23(3):933-49. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.3.933-949.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12529399 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular signaling pathways modulated by low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy.Int J Impot Res. 2019 May;31(3):170-176. doi: 10.1038/s41443-019-0113-3. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Int J Impot Res. 2019. PMID: 30670837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pH sensing by FAK-His58 regulates focal adhesion remodeling.J Cell Biol. 2013 Sep 16;202(6):849-59. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201302131. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24043700 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cell-matrix adhesion by OLA1, the Obg-like ATPase 1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Feb 21;444(4):568-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.099. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24486488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astier A, Avraham H, Manie S N, Groopman J, Canty T, Avraham S, Freedman A S. The related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase is tyrosine-phosphorylated after beta1-integrin stimulation in B cells and binds to p130cas. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:228–232. - PubMed
-
- Astier A, Manie S N, Avraham H, Hirai H, Law S F, Zhang Y, Golemis E A, Fu Y, Druker B J, Haghayeghi N, Freedman A S, Avraham S. The related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase differentially phosphorylates p130Cas and the Cas-like protein, p105HEF1. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19719–19724. - PubMed
-
- Avraham S, London R, Fu Y, Ota S, Hiregowdara D, Li J, Jiang S, Pasztor L M, White R A, Groopman J E, Avraham H. Identification and characterization of a novel related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase (RAFTK) from megakaryocytes and brain. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27742–27751. - PubMed
-
- Bockholt S M, Burridge K. Cell spreading on extracellular matrix proteins induces tyrosine phosphorylation of tensin. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:14565–14567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
