Activation of RNA polymerase III transcription in cells transformed by simian virus 40
- PMID: 10373542
- PMCID: PMC84300
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.4927
Activation of RNA polymerase III transcription in cells transformed by simian virus 40
Abstract
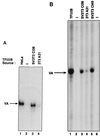
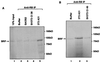
RNA polymerase (Pol) III transcription is abnormally active in fibroblasts that have been transformed by simian virus 40 (SV40). This report presents evidence that two separate components of the general Pol III transcription apparatus, TFIIIB and TFIIIC2, are deregulated following SV40 transformation. TFIIIC2 subunits are expressed at abnormally high levels in SV40-transformed cells, an effect which is observed at both protein and mRNA levels. In untransformed fibroblasts, TFIIIB is subject to repression through association with the retinoblastoma protein RB. The interaction between RB and TFIIIB is compromised following SV40 transformation. Furthermore, the large T antigen of SV40 is shown to relieve repression by RB. The E7 oncoprotein of human papillomavirus can also activate Pol III transcription, an effect that is dependent on its ability to bind to RB. The data provide evidence that both TFIIIB and TFIIIC2 are targets for activation by DNA tumor viruses.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Multiple mechanisms contribute to the activation of RNA polymerase III transcription in cells transformed by papovaviruses.J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 13;277(50):48182-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M201333200. Epub 2002 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12370195
-
RNA polymerase III transcription repressed by Rb through its interactions with TFIIIB and TFIIIC2.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jun 6;272(23):14755-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.23.14755. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9169441
-
Retinoblastoma protein disrupts interactions required for RNA polymerase III transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;20(24):9192-202. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.24.9192-9202.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11094071 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase III transcription: its control by tumor suppressors and its deregulation by transforming agents.Gene Expr. 2000;9(1-2):15-28. doi: 10.3727/000000001783992713. Gene Expr. 2000. PMID: 11097422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase III transcription and cancer.Oncogene. 2004 Apr 19;23(18):3208-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207547. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15094770 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA polymerase III transcription factor TFIIIC2 is overexpressed in ovarian tumors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Nov 7;97(23):12619-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.230224097. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11058163 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 enhances RNA polymerase III-dependent EBER expression through induction of EBER-associated cellular transcription factors.Mol Cancer. 2010 Sep 15;9:241. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-241. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20843307 Free PMC article.
-
Host Noncoding Retrotransposons Induced by DNA Viruses: a SINE of Infection?J Virol. 2017 Nov 14;91(23):e00982-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00982-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28931686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-type specific regulation of gene expression by simian virus 40 T antigens.Virology. 2009 Mar 30;386(1):183-91. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.12.038. Epub 2009 Feb 8. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19201438 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of the Premature tRNA Landscape by Gammaherpesvirus Infection.mBio. 2020 Dec 15;11(6):e02664-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02664-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33323507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzuherri H M, White R J. Regulation of a TATA-binding protein-associated factor during cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:17166–17171. - PubMed
-
- Boulanger P A, Yoshinaga S K, Berk A J. DNA-binding properties and characterization of human transcription factor TFIIIC2. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:15098–15105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
