Cloning and characterization of two evolutionarily conserved subunits (TFIIIC102 and TFIIIC63) of human TFIIIC and their involvement in functional interactions with TFIIIB and RNA polymerase III
- PMID: 10373544
- PMCID: PMC84305
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.4944
Cloning and characterization of two evolutionarily conserved subunits (TFIIIC102 and TFIIIC63) of human TFIIIC and their involvement in functional interactions with TFIIIB and RNA polymerase III
Abstract
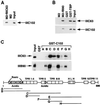
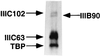
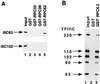
Human transcription factor IIIC (hTFIIIC) is a multisubunit complex that mediates transcription of class III genes through direct recognition of promoters (for tRNA and virus-associated RNA genes) or promoter-TFIIIA complexes (for the 5S RNA gene) and subsequent recruitment of TFIIIB and RNA polymerase III. We describe the cognate cDNA cloning and characterization of two subunits (hTFIIIC63 and hTFIIIC102) that are present within a DNA-binding subcomplex (TFIIIC2) of TFIIIC and are related in structure and function to two yeast TFIIIC subunits (yTFIIIC95 and yTFIIIC131) previously shown to interact, respectively, with the promoter (A box) and with a subunit of yeast TFIIIB. hTFIIIC63 and hTFIIIC102 show parallel in vitro interactions with the homologous human TFIIIB and RNA polymerase III components, as well as additional interactions that may facilitate both TFIIIB and RNA polymerase III recruitment. These include novel interactions of hTFIIIC63 with hTFIIIC102, with hTFIIIB90, and with hRPC62, in addition to the hTFIIIC102-hTFIIIB90 and hTFIIIB90-hRPC39 interactions that parallel the previously described interactions in yeast. As reported for yTFIIIC131, hTFIIIC102 contains acidic and basic regions, tetratricopeptide repeats (TPRs), and a helix-loop-helix domain, and mutagenesis studies have implicated the TPRs in interactions both with hTFIIIC63 and with hTFIIIB90. These observations further document conservation from yeast to human of the structure and function of the RNA polymerase III transcription machinery, but in addition, they provide new insights into the function of hTFIIIC and suggest direct involvement in recruitment of both TFIIIB and RNA polymerase III.
Figures






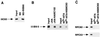

References
-
- Bieker J J, Martin P L, Roeder R G. Formation of a rate-limiting intermediate in 5S RNA gene transcription. Cell. 1985;40:119–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
