The disabled 1 phosphotyrosine-binding domain binds to the internalization signals of transmembrane glycoproteins and to phospholipids
- PMID: 10373567
- PMCID: PMC84361
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.5179
The disabled 1 phosphotyrosine-binding domain binds to the internalization signals of transmembrane glycoproteins and to phospholipids
Abstract
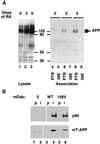
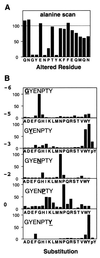
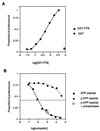
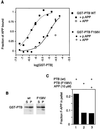
Disabled gene products are important for nervous system development in drosophila and mammals. In mice, the Dab1 protein is thought to function downstream of the extracellular protein Reln during neuronal positioning. The structures of Dab proteins suggest that they mediate protein-protein or protein-membrane docking functions. Here we show that the amino-terminal phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain of Dab1 binds to the transmembrane glycoproteins of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) and low-density lipoprotein receptor families and the cytoplasmic signaling protein Ship. Dab1 associates with the APP cytoplasmic domain in transfected cells and is coexpressed with APP in hippocampal neurons. Screening of a set of altered peptide sequences showed that the sequence GYXNPXY present in APP family members is an optimal binding sequence, with approximately 0.5 microM affinity. Unlike other PTB domains, the Dab1 PTB does not bind to tyrosine-phosphorylated peptide ligands. The PTB domain also binds specifically to phospholipid bilayers containing phosphatidylinositol 4P (PtdIns4P) or PtdIns4,5P2 in a manner that does not interfere with protein binding. We propose that the PTB domain permits Dab1 to bind specifically to transmembrane proteins containing an NPXY internalization signal.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Disabled-1 binds to the cytoplasmic domain of amyloid precursor-like protein 1.J Neurosci. 1999 Sep 1;19(17):7507-15. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-17-07507.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10460257 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of the Dab homology domains of mouse disabled 1 and 2.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 19;278(38):36572-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304384200. Epub 2003 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12826668
-
The phosphotyrosine interaction domains of X11 and FE65 bind to distinct sites on the YENPTY motif of amyloid precursor protein.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Nov;16(11):6229-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.11.6229. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8887653 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoinositide binding by the disabled-1 PTB domain is necessary for membrane localization and Reelin signal transduction.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 11;280(10):9671-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413356200. Epub 2005 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15632144
-
Structural and evolutionary division of phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domains.J Mol Biol. 2005 Jan 7;345(1):1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.10.038. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15567406 Review.
Cited by
-
Canonical and Non-canonical Reelin Signaling.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Jun 30;10:166. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00166. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27445693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The involvement of Reelin in neurodevelopmental disorders.Neuropharmacology. 2013 May;68:122-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.08.015. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 22981949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse disabled 1 regulates the nuclear position of neurons in a Drosophila eye model.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Feb;26(4):1510-7. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.4.1510-1517.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16449660 Free PMC article.
-
Differential reelin-induced enhancement of NMDA and AMPA receptor activity in the adult hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2006 Dec 13;26(50):12943-55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2561-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17167084 Free PMC article.
-
Differential functions of ApoER2 and very low density lipoprotein receptor in Reelin signaling depend on differential sorting of the receptors.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 12;285(7):4896-908. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.025973. Epub 2009 Nov 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19948739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blaikie P, Immanuel D, Wu J, Li N, Yajnik V, Margolis B. A region in Shc distinct from the SH2 domain can bind tyrosine-phosphorylated growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:32031–32034. - PubMed
-
- Borg J-P, Yang Y, De T B M, Margolis B, Turner R S. The X11alpha protein slows cellular amyloid precursor protein processing and reduces Abeta40 and Abeta42 secretion. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14761–14766. - PubMed
-
- Bork P, Margolis B. A phosphotyrosine interaction domain. Cell. 1995;80:693–694. - PubMed
-
- Bressler S L, Gray M D, Sopher B L, Hu Q, Hearn M G, Pham D G, Dinulos M B, Fukuchi K, Sisodia S S, Miller M A, Disteche C M, Martin G M. cDNA cloning and chromosome mapping of the human Fe65 gene: interaction of the conserved cytoplasmic domains of the human beta-amyloid precursor protein and its homologues with the mouse Fe65 protein. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5:1589–1598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
