Trithorax- and Polycomb-group response elements within an Ultrabithorax transcription maintenance unit consist of closely situated but separable sequences
- PMID: 10373568
- PMCID: PMC84362
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.5189
Trithorax- and Polycomb-group response elements within an Ultrabithorax transcription maintenance unit consist of closely situated but separable sequences
Abstract
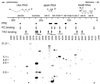
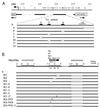
In Drosophila, two classes of genes, the trithorax group and the Polycomb group, are required in concert to maintain gene expression by regulating chromatin structure. We have identified Trithorax protein (TRX) binding elements within the bithorax complex and have found that within the bxd/pbx regulatory region these elements are functionally relevant for normal expression patterns in embryos and confer TRX binding in vivo. TRX was localized to three closely situated sites within a 3-kb chromatin maintenance unit with a modular structure. Results of an in vivo analysis showed that these DNA fragments (each approximately 400 bp) contain both TRX- and Polycomb-group response elements (TREs and PREs) and that in the context of the endogenous Ultrabithorax gene, all of these elements are essential for proper maintenance of expression in embryos. Dissection of one of these maintenance modules showed that TRX- and Polycomb-group responsiveness is conferred by neighboring but separable DNA sequences, suggesting that independent protein complexes are formed at their respective response elements. Furthermore, we have found that the activity of this TRE requires a sequence (approximately 90 bp) which maps to within several tens of base pairs from the closest neighboring PRE and that the PRE activity in one of the elements may require a binding site for PHO, the protein product of the Polycomb-group gene pleiohomeotic. Our results show that long-range maintenance of Ultrabithorax expression requires a complex element composed of cooperating modules, each capable of interacting with both positive and negative chromatin regulators.
Figures
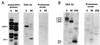
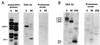


Similar articles
-
Binding of trithorax and Polycomb proteins to the bithorax complex: dynamic changes during early Drosophila embryogenesis.EMBO J. 1998 Sep 1;17(17):5141-50. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.17.5141. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9724650 Free PMC article.
-
Co-localization of Polycomb protein and GAGA factor on regulatory elements responsible for the maintenance of homeotic gene expression.EMBO J. 1997 Jun 16;16(12):3621-32. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.12.3621. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9218803 Free PMC article.
-
GAGA facilitates binding of Pleiohomeotic to a chromatinized Polycomb response element.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jul 15;31(14):4147-56. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg479. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12853632 Free PMC article.
-
Heritable chromatin states induced by the Polycomb and trithorax group genes.Novartis Found Symp. 1998;214:51-61; discussion 61-6, 104-13. doi: 10.1002/9780470515501.ch4. Novartis Found Symp. 1998. PMID: 9601011 Review.
-
The Polycomb group--no longer an exclusive club?Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001 Apr;11(2):175-81. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(00)00176-3. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001. PMID: 11250141 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional network controlled by the trithorax-group gene ash2 in Drosophila melanogaster.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Mar 18;100(6):3293-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0538075100. Epub 2003 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12626737 Free PMC article.
-
MLL repression domain interacts with histone deacetylases, the polycomb group proteins HPC2 and BMI-1, and the corepressor C-terminal-binding protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 8;100(14):8342-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1436338100. Epub 2003 Jun 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12829790 Free PMC article.
-
A double-bromodomain protein, FSH-S, activates the homeotic gene ultrabithorax through a critical promoter-proximal region.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;27(15):5486-98. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00692-07. Epub 2007 May 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17526731 Free PMC article.
-
The Trithorax-mimic allele of Enhancer of zeste renders active domains of target genes accessible to polycomb-group-dependent silencing in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2001 Nov;159(3):1135-50. doi: 10.1093/genetics/159.3.1135. Genetics. 2001. PMID: 11729158 Free PMC article.
-
Long-range repression by multiple polycomb group (PcG) proteins targeted by fusion to a defined DNA-binding domain in Drosophila.Genetics. 2001 May;158(1):291-307. doi: 10.1093/genetics/158.1.291. Genetics. 2001. PMID: 11333237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bender W, Akam M, Karch F, Beachy P A, Peifer M, Spierer P, Lewis I B, Hogness D S. Molecular genetics of the bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1983;221:23–29. - PubMed
-
- Bienz M, Müller J. Transcriptional silencing of homeotic genes in Drosophila. BioEssays. 1995;17:775–784. - PubMed
-
- Breen T R, Harte P J. trithorax regulates multiple homeotic genes in the bithorax and Antennapedia complexes and exerts different tissue-specific, parasegment-specific and promoter-specific effects on each. Development. 1993;117:119–134. - PubMed
-
- Brown J L, Mucci D, Whiteley M, Dirksen M L, Kassis J A. The Drosophila Polycomb group gene pleiohomeotic encodes a DNA binding protein with homology to the transcription factor YY1. Mol Cell. 1998;1:1057–1064. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
