PPARalpha activators inhibit cytokine-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human endothelial cells
- PMID: 10377075
- PMCID: PMC4231776
- DOI: 10.1161/01.cir.99.24.3125
PPARalpha activators inhibit cytokine-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Adhesion molecule expression on the endothelial cell (EC) surface is critical for leukocyte recruitment to atherosclerotic lesions. Better understanding of transcriptional regulation of adhesion molecules in ECs may provide important insight into plaque formation. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPARalpha), a member of the nuclear receptor family, regulates gene expression in response to certain fatty acids and fibric acid derivatives. The present study investigated PPARalpha expression in human ECs and their regulation of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1).
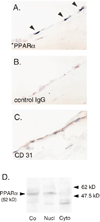
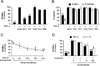
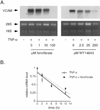
Methods and results: Immunohistochemistry revealed that human carotid artery ECs express PPARalpha. Pretreatment of cultured human ECs with the PPARalpha activators fenofibrate or WY14643 inhibited TNF-alpha-induced VCAM-1 in a time- and concentration-dependent manner, an effect not seen with PPARgamma activators. Both PPARalpha activators decreased cytokine-induced VCAM-1 mRNA expression without altering its mRNA half-life. Transient transfection of deletional VCAM-1 promoter constructs and electrophoretic mobility shift assays suggest that fenofibrate inhibits VCAM-1 transcription in part by inhibiting NF-kappaB. Finally, PPARalpha activators significantly reduced adhesion of U937 cells to cultured human ECs.
Conclusions: Human ECs express PPARalpha, a potentially important regulator of atherogenesis through its transcriptional control of VCAM-1 gene expression. Such findings also have implications regarding the clinical use of lipid-lowering agents, like fibric acids, which can activate PPARalpha.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel thiazolidinedione MCC-555 down-regulates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in vascular endothelial cells.Atherosclerosis. 2005 Sep;182(1):71-7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.02.004. Epub 2005 Mar 4. Atherosclerosis. 2005. PMID: 16115476
-
PPARalpha and GR differentially down-regulate the expression of nuclear factor-kappaB-responsive genes in vascular endothelial cells.Endocrinology. 2001 Aug;142(8):3332-9. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.8.8340. Endocrinology. 2001. PMID: 11459775
-
PPARalpha activators inhibit tissue factor expression and activity in human monocytes.Circulation. 2001 Jan 16;103(2):213-9. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.2.213. Circulation. 2001. PMID: 11208679
-
Role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) in atherosclerosis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Oct 15;60(8):1245-50. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00430-5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11007963 Review.
-
Pleiotropic actions of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002 May 1;22(5):717-26. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.0000015598.86369.04. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002. PMID: 12006382 Review.
Cited by
-
Fibrates and cholestasis.Hepatology. 2015 Aug;62(2):635-43. doi: 10.1002/hep.27744. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25678132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fenofibric acid: a new fibrate approved for use in combination with statin for the treatment of mixed dyslipidemia.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010 May 25;6:351-62. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s6714. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010. PMID: 20531954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fenofibrate for patients with asymptomatic primary biliary cirrhosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Mar 15;10(6):894-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i6.894. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15040040 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
PPARalpha: an emerging therapeutic target in diabetic microvascular damage.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010 Aug;6(8):454-63. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2010.89. Epub 2010 Jun 22. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20567246 Review.
-
Insulin resistance, diabetes, and atherosclerosis: thiazolidinediones as therapeutic interventions.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2002 Nov;4(6):514-21. doi: 10.1007/s11886-002-0116-3. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2002. PMID: 12379175 Review.
References
-
- Poole JCF, Florey HW. Changes in the endothelium of the aorta and the behavior of macrophages in experimental atheroma of rabbits. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958;75:245–253. - PubMed
-
- Faggiotto A, Ross R, Harker L. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate, I: changes that lead to fatty streak formation. Arteriosclerosis. 1984;4:323–340. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Cybulsky MI, Gimbrone MA, Jr, Libby P. An atherogenic diet rapidly induces VCAM-1, a cytokine-regulatable mononuclear leukocyte adhesion molecule, in rabbit aortic endothelium. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993;13:197–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

