Voltage-dependent neuromodulation of Na+ channels by D1-like dopamine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 10377341
- PMCID: PMC6782346
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-13-05301.1999
Voltage-dependent neuromodulation of Na+ channels by D1-like dopamine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons
Abstract
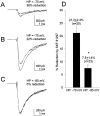
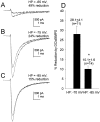
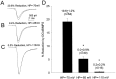
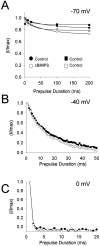
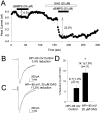
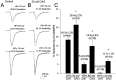
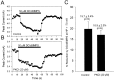
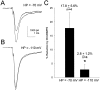
Activation of D1-like dopamine (DA) receptors reduces peak Na+ current in acutely isolated hippocampal neurons through phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of the Na+ channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). Here we report that neuromodulation of Na+ currents by DA receptors via PKA is voltage-dependent in the range of -110 to -70 mV and is also sensitive to concurrent activation of protein kinase C (PKC). Depolarization enhanced the ability of D1-like DA receptors to reduce peak Na+ currents via the PKA pathway. Similar voltage-dependent modulation was observed when PKA was activated directly with the membrane-permeant PKA activator DCl-cBIMPS (cBIMPS; 20 microM), indicating that the membrane potential dependence occurs downstream of PKA. PKA activation caused only a small (-2.9 mV) shift in the voltage dependence of steady-state inactivation and had no effect on slow inactivation or on the rates of entry into the fast or slow inactivated states, suggesting that another mechanism is responsible for coupling of membrane potential changes to PKA modulation. Activation of PKC with a low concentration of the membrane-permeant diacylglycerol analog oleylacetyl glycerol also potentiated modulation by SKF 81297 or cBIMPS, and these effects were most striking at hyperpolarized membrane potentials where PKA modulation was not stimulated by membrane depolarization. Thus, activation of D1-like DA receptors causes a strong reduction in Na+ current via the PKA pathway, but it is effective primarily when it is combined with depolarization or activation of PKC. The convergence of these three distinct signaling modalities on the Na+ channel provides an intriguing mechanism for integration of information from multiple signaling pathways in the hippocampus and CNS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dopaminergic modulation of voltage-gated Na+ current in rat hippocampal neurons requires anchoring of cAMP-dependent protein kinase.J Neurosci. 1999 Sep 1;19(17):RC21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-17-j0003.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10460275 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of convergent regulation of brain Na(+) channels by protein kinase C and protein kinase A anchored to AKAP-15.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002 Sep;21(1):63-80. doi: 10.1006/mcne.2002.1162. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12359152
-
Dopamine D1/D5 receptor activation modulates a persistent sodium current in rat prefrontal cortical neurons in vitro.J Neurophysiol. 2000 Jul;84(1):75-87. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.84.1.75. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 10899185
-
Molecular properties of brain sodium channels: an important target for anticonvulsant drugs.Adv Neurol. 1999;79:441-56. Adv Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10514834 Review.
-
The role of D1 dopamine receptors and phospho-ERK in mediating cytotoxicity. Commentary.Neurotox Res. 2005;7(3):179-81. doi: 10.1007/BF03036447. Neurotox Res. 2005. PMID: 15897152 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution and divergence of sodium channel genes in vertebrates.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jun 19;98(13):7588-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.131171798. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11416226 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of α-cell glucagon secretion: The role of second messengers.Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2022 Mar 6;8(1):7-18. doi: 10.1016/j.cdtm.2021.06.001. eCollection 2022 Mar. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35620162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine D1-class receptors selectively modulate a slowly inactivating potassium current in rat medial prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons.J Neurosci. 2003 Apr 1;23(7):2686-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02686.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12684454 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated amphetamine administration decreases D1 dopamine receptor-mediated inhibition of voltage-gated sodium currents in the prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 22;26(12):3164-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2375-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16554467 Free PMC article.
-
Amplitude-dependent spike-broadening and enhanced Ca(2+) signaling in GnRH-secreting neurons.Biophys J. 2000 Sep;79(3):1310-23. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76384-3. Biophys J. 2000. PMID: 10968994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cantrell AR, Ma JY, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Muscarinic modulation of sodium current by activation of protein kinase C in rat hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1996;16:1019–1026. - PubMed
-
- Civelli O, Bunzow JR, Grandy DK. Molecular diversity of the dopamine receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;32:281–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
