The Caenorhabditis elegans unc-49 locus encodes multiple subunits of a heteromultimeric GABA receptor
- PMID: 10377345
- PMCID: PMC6782323
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-13-05348.1999
The Caenorhabditis elegans unc-49 locus encodes multiple subunits of a heteromultimeric GABA receptor
Abstract
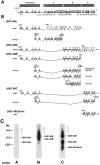
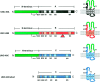
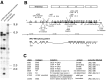
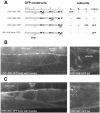
Ionotropic GABA receptors generally require the products of three subunit genes. By contrast, the GABA receptor needed for locomotion in Caenorhabditis elegans requires only the unc-49 gene. We cloned unc-49 and demonstrated that it possesses an unusual overlapping gene structure. unc-49 contains a single copy of a GABA receptor N terminus, followed by three tandem copies of a GABA receptor C terminus. Using a single promoter, unc-49 generates three distinct GABAA receptor-like subunits by splicing the N terminus to each of the three C-terminal repeats. This organization suggests that the three UNC-49 subunits (UNC-49A, UNC-49B, and UNC-49C) are coordinately rescued and therefore might coassemble to form a heteromultimeric GABA receptor. Surprisingly, only UNC-49B and UNC-49C are expressed at high levels, whereas UNC-49A expression is barely detectable. Green fluorescent protein-tagged UNC-49B and UNC-49C subunits are coexpressed in muscle cells and are colocalized to synaptic regions. UNC-49B and UNC-49C also coassemble efficiently in Xenopus oocytes and HEK-293 cells to form a heteromeric GABA receptor. Together these data argue that UNC-49B and UNC-49C coassemble at the C. elegans neuromuscular junction. Thus, C. elegans is able to encode a heteromeric GABA receptor with a single locus.
Figures


References
-
- Alfonso A, Grundahl K, McManus JR, Asbury JM, Rand JB. Alternative splicing leads to two cholinergic proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1994;241:627–630. - PubMed
-
- Amin J, Weiss DS. Homomeric ρ1 GABA channels: activation properties and domains. Receptors Channels. 1994;2:227–236. - PubMed
-
- Amin J, Weiss DS. GABAA receptor needs two homologous domains of the beta-subunit for activation by GABA but not by pentobarbital. Nature. 1993;366:565–569. - PubMed
-
- Andres AJ, Thummel CS. Methods for quantitative analysis of transcription in larvae and prepupae. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;44:565–573. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley; New York: 1995.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
