Cdc20 associates with the kinase aurora2/Aik
- PMID: 10377410
- PMCID: PMC22081
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.13.7306
Cdc20 associates with the kinase aurora2/Aik
Abstract
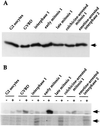
Cdc20/fizzy family proteins are involved in activation of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome, which catalyzes the ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of cell cycle regulatory proteins such as anaphase inhibitors and mitotic cyclins, leading to chromosome segregation and exit from mitosis. Previous work has shown that human Cdc20 (hCdc20/p55CDC) associates with one or more kinases. We report here that Cdc20-associated myelin basic protein kinase activity peaks sharply in early M phase (embryonic cells) or in G2 phase (somatic cells). In HeLa cells, Cdc20 is associated with the kinase aurora2/Aik. Aurora2/Aik is a member of the aurora/Ipl1 family of kinases that, like Cdc20, previously has been shown to be localized at mitotic spindle poles and is involved in regulating chromosome segregation and maintaining genomic stability. The demonstration that Cdc20 is associated with aurora2/Aik suggests that some function of Cdc20 is carried out or regulated through its association with aurora2/Aik.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cell cycle-dependent expression and spindle pole localization of a novel human protein kinase, Aik, related to Aurora of Drosophila and yeast Ipl1.J Biol Chem. 1997 May 23;272(21):13766-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.21.13766. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9153231
-
Bub1 and aurora B cooperate to maintain BubR1-mediated inhibition of APC/CCdc20.J Cell Sci. 2005 Aug 15;118(Pt 16):3639-52. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02487. Epub 2005 Jul 26. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16046481
-
Activation of the human anaphase-promoting complex by proteins of the CDC20/Fizzy family.Curr Biol. 1998 Nov 5;8(22):1207-10. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(07)00510-6. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9811605
-
Cdc20: At the Crossroads between Chromosome Segregation and Mitotic Exit.Trends Biochem Sci. 2017 Mar;42(3):193-205. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.12.001. Epub 2017 Feb 12. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28202332 Review.
-
Bub1 and the multilayered inhibition of Cdc20-APC/C in mitosis.Trends Cell Biol. 2005 May;15(5):231-3. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.03.003. Trends Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15866025 Review.
Cited by
-
Quercetin suppresses lung cancer growth by targeting Aurora B kinase.Cancer Med. 2016 Nov;5(11):3156-3165. doi: 10.1002/cam4.891. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 27704720 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of phosphorylated residues that affect the activity of the mitotic kinase Aurora-A.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Nov 26;99(24):15440-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.202606599. Epub 2002 Nov 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12422018 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of p160ROCK bypasses cell cycle arrest after Aurora-A/STK15 depletion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 15;101(24):8975-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308484101. Epub 2004 Jun 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15178765 Free PMC article.
-
Plk1 regulates mitotic Aurora A function through betaTrCP-dependent degradation of hBora.Chromosoma. 2008 Oct;117(5):457-69. doi: 10.1007/s00412-008-0165-5. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Chromosoma. 2008. PMID: 18521620 Free PMC article.
-
Biphasic activation of Aurora-A kinase during the meiosis I- meiosis II transition in Xenopus oocytes.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Mar;23(5):1703-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.5.1703-1716.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12588989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Finley D, Chau V. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:25–69. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807. - PubMed
-
- King R, Peters J, Tugendreich S M, Rolfe M, Hieter P, Kirschner M W. Cell. 1995;81:279–288. - PubMed
-
- Irniger S, Piatti S, Michaelis C, Nasmyth K. Cell. 1995;81:269–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

