Disruption of mRad50 causes embryonic stem cell lethality, abnormal embryonic development, and sensitivity to ionizing radiation
- PMID: 10377422
- PMCID: PMC22093
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.13.7376
Disruption of mRad50 causes embryonic stem cell lethality, abnormal embryonic development, and sensitivity to ionizing radiation
Abstract
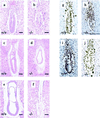
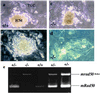
The Mre11/Rad50 protein complex functions in diverse aspects of the cellular response to double-strand breaks (DSBs), including the detection of DNA damage, the activation of cell cycle checkpoints, and DSB repair. Whereas genetic analyses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae have provided insight regarding DSB repair functions of this highly conserved complex, the implication of the human complex in Nijmegen breakage syndrome reveals its role in cell cycle checkpoint functions. We established mRad50 mutant mice to examine the role of the mammalian Mre11/Rad50 protein complex in the DNA damage response. Early embryonic cells deficient in mRad50 are hypersensitive to ionizing radiation, consistent with a role for this complex in the repair of ionizing radiation-induced DSBs. However, the null mrad50 mutation is lethal in cultured embryonic stem cells and in early developing embryos, indicating that the mammalian Mre11/Rad50 protein complex mediates functions in normally growing cells that are essential for viability.
Figures

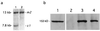
Similar articles
-
Checkpoint activation in response to double-strand breaks requires the Mre11/Rad50/Xrs2 complex.Nat Cell Biol. 2001 Sep;3(9):844-7. doi: 10.1038/ncb0901-844. Nat Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11533665
-
Mutations in the MRE11, RAD50, XRS2, and MRE2 genes alter chromatin configuration at meiotic DNA double-stranded break sites in premeiotic and meiotic cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jan 20;95(2):646-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.2.646. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9435246 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of the Mre11 complex and exonuclease 1 for activation of the Mec1 signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(22):10016-25. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.10016-10025.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15509802 Free PMC article.
-
[Functional regulation of the Mre11/Rad50/Xrs2 complex in the processes of recombination and DSB repair].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2001 Jun;46(8 Suppl):1030-7. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2001. PMID: 11436290 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
The Mre11 complex: at the crossroads of dna repair and checkpoint signalling.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;3(5):317-27. doi: 10.1038/nrm805. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11988766 Review.
Cited by
-
Mre11 complex and DNA replication: linkage to E2F and sites of DNA synthesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Sep;21(17):6006-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.17.6006-6016.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11486038 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of germline mutations in cancer susceptibility genes in Chinese patients with renal cell carcinoma.Transl Androl Urol. 2023 Feb 28;12(2):308-319. doi: 10.21037/tau-23-32. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Transl Androl Urol. 2023. PMID: 36915884 Free PMC article.
-
Developing master keys to brain pathology, cancer and aging from the structural biology of proteins controlling reactive oxygen species and DNA repair.Neuroscience. 2007 Apr 14;145(4):1280-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.10.045. Epub 2006 Dec 15. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17174478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse Rad9b is essential for embryonic development and promotes resistance to DNA damage.Dev Dyn. 2010 Nov;239(11):2837-50. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22415. Dev Dyn. 2010. PMID: 20842695 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing somatic hypermutation in Ramos B cells after overexpression or knockdown of specific genes.J Vis Exp. 2011 Nov 1;(57):e3573. doi: 10.3791/3573. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 22083360 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

