Induction of differentiation of pre-NKT cells to mature Valpha14 NKT cells by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- PMID: 10377433
- PMCID: PMC22104
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.13.7439
Induction of differentiation of pre-NKT cells to mature Valpha14 NKT cells by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor
Abstract
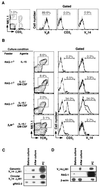
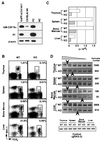
Valpha14 NKT cells express an invariant antigen receptor encoded by Valpha14 and Jalpha281 gene segments as well as natural killer (NK) markers, including NK1.1. Here, we describe a precursor population of NKT cells (pre-NKT) that expresses NK1.1, T cell antigen receptor beta, pTalpha, and RAG1/2 but not Valpha14 and surface CD3epsilon. Such pre-NKT cells were differentiated successfully in vitro into mature CD3epsilon+ Valpha14(+) NKT cells by IL-15 and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in conjunction with stroma cells. Interestingly, only GM-CSF without stroma cells induced the Valpha14-Jalpha281 gene rearrangement in the pre-NKT cells. This also was confirmed by the findings that the number of mature Valpha14 NKT cells and the frequency of Valpha14-Jalpha281 rearrangements were decreased significantly in the mice lacking a GM-CSF receptor component, common beta-chain. These results suggest a crucial role of GM-CSF in the development of Valpha14 NKT cells in vivo.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

