Cutaneous reflexes of the human leg during passive movement
- PMID: 10381606
- PMCID: PMC2269424
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0619p.x
Cutaneous reflexes of the human leg during passive movement
Abstract
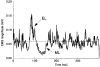
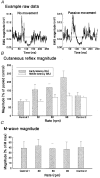
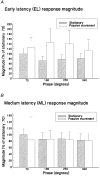
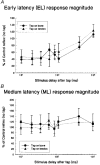
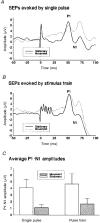
1. Four experiments tested the hypothesis that movement-induced discharge of somatosensory receptors attenuates cutaneous reflexes in the human lower limb. In the first experiment, cutaneous reflexes were evoked in the isometrically contracting tibialis anterior muscle (TA) by a train of stimuli to the tibial nerve at the ankle. The constancy of stimulus amplitudes was indirectly verified by monitoring M waves elicited in the abductor hallucis muscle. There was a small increase in the reflex excitation (early latency, EL) during passive cycling movement of the leg compared with when the leg was stationary, a result opposite to that hypothesized. There was no significant effect on the magnitude of the subsequent inhibitory reflex component (middle latency, ML), even with increased rate of movement, or on the latency of any of the reflex components. 2. In the second experiment, the two reflex components (EL and ML) elicited in TA at four positions in the movement cycle were compared with corresponding reflexes elicited with the limb stationary at those positions. Despite the markedly different degree of stretch of the leg muscles, movement phase exerted no statistically significant effect on EL or ML reflex magnitudes. 3. In the third experiment, taps to the quadriceps tendon, to elicit muscle spindle discharge, had no effect on the magnitude of ML in TA muscle. The conditioning attenuated EL magnitude for the first 110 ms. Tendon tap to the skin over the tibia revealed similar attenuation of EL. 4. The sural nerve was stimulated at the ankle in the fourth experiment. TA EMG reflex excitatory and inhibitory responses still showed no significant attenuation with passive movement. Initial somatosensory evoked potentials (SEPs), measured from scalp electrodes, were attenuated by movement. 5. The results indicate that there is separate control of transmission in Ia and cutaneous pathways during leg movement. This suggests that modulation of the cutaneous reflex during locomotion is not the result of inhibition arising from motion-related sensory receptor discharge.
Figures
References
-
- Brooke JD, Cheng J, Collins D, McIlroy WE, Misiaszek J, Staines WR. Sensori-sensory afferent conditioning with leg movement: gain control in spinal reflex and ascending paths. Progress in Neurobiology. 1997a;51:393–421. - PubMed
-
- Brooke JD, Cheng J, Misiaszek JE, Lafferty K. Amplitude modulation of the soleus H reflex in the human during active and passive stepping movements. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1995a;73:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Brooke JD, McIlroy WE, Angerilli PA, Peritore GF, Staines WR. XXXIIIth International Congress of the Physiological Sciences. Russia: St Petersburg; 1997b. Separation in control of cutaneous versus spinal paths in humans; p. P078·02.
-
- Brooke JD, McIlroy WE, Collins DF, Misiaszek JE. Mechanisms within the human spinal cord suppress fast reflexes to control the movement of the legs. Brain Research. 1995b;679:255–260. - PubMed
-
- Brooke JD, Misiaszek JE, Cheng J. Locomotor-like rotation of either hip or knee inhibits soleus H-reflexes in humans. Somatosensory and Motor Research. 1993;10:316–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

