Evaluation of corneal thickness and topography in normal eyes using the Orbscan corneal topography system
- PMID: 10381661
- PMCID: PMC1723104
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.83.7.774
Evaluation of corneal thickness and topography in normal eyes using the Orbscan corneal topography system
Abstract
Aims: To map the thickness, elevation (anterior and posterior corneal surface), and axial curvature of the cornea in normal eyes with the Orbscan corneal topography system.
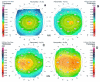
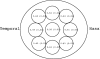
Methods: 94 eyes of 51 normal subjects were investigated using the Orbscan corneal topography system. The anterior and posterior corneal elevation maps were classified into regular ridge, irregular ridge, incomplete ridge, island, and unclassified patterns, and the axial power maps were grouped into round, oval, symmetric bow tie, asymmetric bow tie, and irregular patterns. The pachymetry patterns were designated as round, oval, decentred round, and decentred oval.
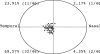
Results: The thinnest point on the cornea was located at an average of 0.90 (SD 0. 51) mm from visual axis and had an average thickness of 0.55 (0.03) mm. In 69.57% of eyes, this point was located in the inferotemporal quadrant, followed by the superotemporal quadrant in 23.91%, the inferonasal quadrant in 4.35%, and the superonasal quadrant in 2.17%. Among the nine regions of the cornea evaluated (central, superotemporal, temporal, inferotemporal, inferior, inferonasal, nasal, superonasal, and superior) the central cornea had the lowest average thickness (0.56 (0.03) mm) and the superior cornea had the greatest average thickness (0.64 (0.03) mm). The mean simulated keratometry (SimK) was 44.24 (1.61)/43.31 (1.66) dioptres (D) and the mean astigmatism was 0.90 (0.41) D. Island (71.74%) was the most common elevation pattern observed in the anterior corneal surface, followed by incomplete ridge (19.57%), regular ridge (4.34%), irregular ridge (2.17%), and unclassified (2.17%). Island (32.61%) was the most common topographic pattern in the posterior corneal surface, following by regular ridge (30.43%), incomplete ridge (23. 91%), and irregular ridge (13.04%) patterns. Symmetric bow tie was the most common axial power pattern in the anterior cornea (39.13%), followed by oval (26.07%), asymmetric bow tie (23.91%), round (6. 52%), and irregular (4.53%) patterns. In the pachymetry maps, 47.83% of eyes had an oval pattern, and round, decentred oval, and decentred round were observed in 41.30%, 8.70%, and 2.18% of eyes, respectively.
Conclusion: The information on regional corneal thickness, corneal elevation and axial corneal curvature obtained with the Orbscan corneal topography system from normal eyes provides a reference for comparison with diseased corneas. The Orbscan corneal topography system is a useful tool to evaluate both corneal topography and corneal thickness.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
