Comparison of the levels of hepatocyte growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in aqueous fluid and serum with grades of retinopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 10381671
- PMCID: PMC1723111
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.83.7.834
Comparison of the levels of hepatocyte growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in aqueous fluid and serum with grades of retinopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Aims: To determine the relation between the stages of diabetic retinopathy (DR) and the levels of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in aqueous fluid and serum.
Methods: Levels of HGF and VEGF in serum and aqueous humour obtained during ocular surgery were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay in 58 diabetic patients with 32 non-diabetic patients (NDM) as controls. The patients with diabetes were classified into three groups according to the stage of DR: no DR (NDR; 15 cases), non-proliferative DR (NPDR; six cases), and proliferative DR (PDR; 37 cases).
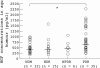
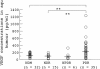
Results: No significant differences were found between any of the groups in serum concentrations of HGF or VEGF. The aqueous HGF levels increased with the stage of DR: NDM, median 397 pg/ml, range 133-930 pg/ml; NDR, 371 pg/ml, 142-1536 pg/ml; NPDR, 455 pg/ml, 162-1007 pg/ml; and PDR, 638 pg/ml, 187-2222 pg/ml. The aqueous VEGF levels in PDR (median 212 pg/ml, range 14-1216 pg/ml) were significantly higher than in NDM (105 pg/ml, 9-203 pg/ml), but aqueous HGF concentrations were unrelated to those of VEGF.
Conclusion: The results of the present study suggest that both HGF and VEGF present in the ocular tissues may play important roles in the progression of DR.
Figures
Comment in
-
A role for hepatocyte growth factor in diabetic retinopathy?Br J Ophthalmol. 1999 Jul;83(7):763-4. doi: 10.1136/bjo.83.7.763. Br J Ophthalmol. 1999. PMID: 10381657 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
