The efficacy of a novel adenosine agonist (WAG 994) in postoperative dental pain
- PMID: 10383546
- PMCID: PMC2014251
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1999.00963.x
The efficacy of a novel adenosine agonist (WAG 994) in postoperative dental pain
Abstract
Aims: To determine the comparative efficacy of a new novel adenosine agonist (WAG 994) in postoperative pain after third molar surgery.
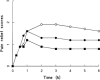
Methods: One hundred and twenty-two patients with postoperative pain after third molar surgery were randomised in a placebo double-blind trial with an active control group. In the early postoperative period patients received either a single dose of WAG 994 1 mg, ibuprofen 400 mg or matched placebos. Pain intensity score was recorded on serial visual analogue scales over a 6 h investigation period. Similarly, pain relief was completed on a 4 point categorical scale at each evaluation point. Patients had access to escape analgesic and if these were taken, the time and dosage were recorded. A sparse sampling technique was used to investigate the relationship between analgesic effects and plasma concentrations of WAG 994.
Results: All three treatment groups were matched for various demographic variables. For all efficacy measures, WAG 994 was not significantly different from placebo (P >0.05), whereas ibuprofen 400 mg was significantly superior to placebo (P<0.001). No significant relationships (P<0.05) were found between WAG 994 pharmacokinetic variables and efficacy measures. Conclusion WAG 994, an adenosine agonist, did not show efficacy in the management of postoperative pain after third molar surgery. Although this pain responds well to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it appears to be resistant to compounds that interact with purinergic receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The comparative efficacy of aceclofenac and ibuprofen in postoperative pain after third molar surgery.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998 Oct;36(5):375-9. doi: 10.1016/s0266-4356(98)90650-7. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998. PMID: 9831059 Clinical Trial.
-
Multicentre evaluation of the adenosine agonist GR79236X in patients with dental pain after third molar extraction.Br J Anaesth. 2007 May;98(5):672-6. doi: 10.1093/bja/aem075. Epub 2007 Apr 7. Br J Anaesth. 2007. PMID: 17416906 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Analgesic Effects of Ibuprofen, Celecoxib and Tramadol after third Molar Surgery: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018 Nov 1;19(11):1334-1340. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018. PMID: 30602637 Clinical Trial.
-
Analgesic efficacy and tolerability of oxycodone 5 mg/ibuprofen 400 mg compared with those of oxycodone 5 mg/acetaminophen 325 mg and hydrocodone 7.5 mg/acetaminophen 500 mg in patients with moderate to severe postoperative pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-dose, parallel-group study in a dental pain model.Clin Ther. 2005 Apr;27(4):418-29. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.04.010. Clin Ther. 2005. PMID: 15922815 Clinical Trial.
-
A single-tablet fixed-dose combination of racemic ibuprofen/paracetamol in the management of moderate to severe postoperative dental pain in adult and adolescent patients: a multicenter, two-stage, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, factorial study.Clin Ther. 2010 Jun;32(6):1033-49. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.06.002. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20637958 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The effects of intraoperative adenosine infusion on acute opioid tolerance and opioid induced hyperalgesia induced by remifentanil in adult patients undergoing tonsillectomy.Korean J Pain. 2011 Mar;24(1):7-12. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.1.7. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Korean J Pain. 2011. PMID: 21390173 Free PMC article.
-
Single dose oral ibuprofen for acute postoperative pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jul 8;2009(3):CD001548. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001548.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 19588326 Free PMC article.
-
The adenosine A1 receptor agonist WAG 994 suppresses acute kainic acid-induced status epilepticus in vivo.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Oct 1;176:108213. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108213. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32615188 Free PMC article.
-
From purines to purinergic signalling: molecular functions and human diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Apr 28;6(1):162. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00553-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33907179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical application of adenosine and ATP for pain control.J Anesth. 2005;19(3):225-35. doi: 10.1007/s00540-005-0310-8. J Anesth. 2005. PMID: 16032451 Review.
References
-
- Williams M. Purine receptors in mammalian tissues: pharmacology and functional significance. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:315–435. - PubMed
-
- Stiles GL. Adenosine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:6451–6454. - PubMed
-
- Karlson R, Gordh T, Hartvig P, Claeo P. Effects of intrathecal injection of the adenosine receptor agonist R-phenylisopropyl-adenosine and N-ethylcarboxamide-adenosine on nociception and motor function in the rat. Anesth Analg. 1990;71:60–64. - PubMed
-
- Sawynok J, Sweeney MI. The role of purines in nociception. Neuroscience. 1989;32:557–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources