Population pharmacokinetics of methadone in opiate users: characterization of time-dependent changes
- PMID: 10383559
- PMCID: PMC2014882
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1999.00974.x
Population pharmacokinetics of methadone in opiate users: characterization of time-dependent changes
Abstract
Aims: Although methadone is widely used to treat opiate dependence, guidelines for its dosage are poorly defined. There is increasing evidence to suggest that a strategy based on plasma drug monitoring may be useful to detect non-compliance. Therefore, we have developed a population-based pharmacokinetic (POP-PK) model that characterises adaptive changes in methadone kinetics.
Methods: Sparse plasma rac-methadone concentrations measured in 35 opiate-users were assessed using the P-Pharm software. The final structural model comprised a biexponential function with first-order input and allowance for time-dependent change in both clearance (CL) and initial volume of distribution (V ). Values of these parameters were allowed to increase or decrease exponentially to an asymptotic value.
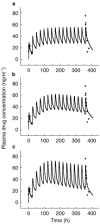
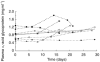
Results: Increase in individual values of CL and increase or decrease in individual values of V with time was observed in applying the model to the experimental data.
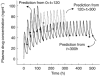
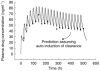
Conclusions: A time-dependent increase in the clearance of methadone is consistent with auto-induction of CYP3A4, the enzyme responsible for much of the metabolism of the drug. The changes in V with time might reflect both up- and down-regulation of alpha1-acid glycoprotein, the major plasma binding site for methadone. By accounting for adaptive kinetic changes, the POP-PK model provides an improved basis for forecasting plasma methadone concentrations to predict and adjust dosage of the drug and to monitor compliance in opiate-users on maintenance treatment.
Figures
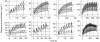
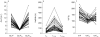
Similar articles
-
The pharmacokinetics of methadone in healthy subjects and opiate users.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1997 Oct;44(4):325-34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1997.t01-1-00591.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9354306 Free PMC article.
-
Population-based pharmacokinetic approach for methadone monitoring of opiate addicts: potential clinical utility.Addiction. 2000 Dec;95(12):1771-83. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.2000.951217717.x. Addiction. 2000. PMID: 11177493
-
The optimization of methadone dosing whilst treating with rifampicin: A pharmacokinetic modeling study.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019 Jul 1;200:168-180. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.03.013. Epub 2019 May 20. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019. PMID: 31122724
-
Interindividual variability of the clinical pharmacokinetics of methadone: implications for the treatment of opioid dependence.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41(14):1153-93. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200241140-00003. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002. PMID: 12405865 Review.
-
Maintenance medication for opiate addiction: the foundation of recovery.J Addict Dis. 2012;31(3):207-25. doi: 10.1080/10550887.2012.694598. J Addict Dis. 2012. PMID: 22873183 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of autoinduction of methadone N-demethylation in human hepatocytes.Anesth Analg. 2013 Jul;117(1):52-60. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182918252. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Anesth Analg. 2013. PMID: 23733841 Free PMC article.
-
Changes to methadone clearance during pregnancy.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Nov;61(10):763-8. doi: 10.1007/s00228-005-0035-5. Epub 2005 Oct 29. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16261362
-
Neonatal abstinence syndrome: treatment and pediatric outcomes.Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Mar;56(1):186-92. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0b013e31827feea4. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2013. PMID: 23314720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A discordance between cytochrome P450 2D6 genotype and phenotype in patients undergoing methadone maintenance treatment.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003 Aug;56(2):220-4. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01851.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12895196 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Sampling Strategies for Cytochrome P450 Phenotyping.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016 Feb;55(2):169-84. doi: 10.1007/s40262-015-0306-y. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016. PMID: 26239501 Review.
References
-
- Wolff K, Hay AWM. Plasma methadone monitoring with methadone maintenance treatment. Drug Alcohol Dependence. 1994;36:69–71. - PubMed
-
- Nilsson MI, Gronbladh L, Wilderlov E, Anggard E. Pharmacokinetics of methadone in methadone maintenance treatment: Characterisation of therapeutic failures. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;25:497–501. - PubMed
-
- Loimer N, Schmid R. The use of plasma levels to optimise methadone maintenance treatment. Drug Alcohol Dependence. 1992;30:241–246. - PubMed
-
- Eap CB, Finkbeiner T, Gastpar M, Scherbaum N, Powell K, Baumann P. Replacement of (R)-methadone by a double dose of (R, S)-methadone in addicts: Inter-individual variability of the (R)/(S) ratios and evidence of adaptive changes in methadone pharmacokinetics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1996;50:385–389. - PubMed
-
- De Vos JW, Ufkes JGR, Van Brussel GHA, Van Den Brink W. Craving despite extremely high methadone dose. Drug Alcohol Dependence. 1996;40:181–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

