Suppressive effect of distinct bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist on allergen-evoked exudation and leukocyte infiltration in sensitized rats
- PMID: 10385228
- PMCID: PMC1566018
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702536
Suppressive effect of distinct bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist on allergen-evoked exudation and leukocyte infiltration in sensitized rats
Abstract
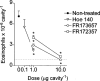
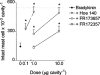
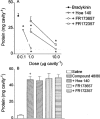
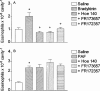
1. Bradykinin is suggested to play a role in the pathophysiology of several acute and chronic diseases, including allergic disorders such as asthma. In the present study, we have investigated the importance of bradykinin in mediating allergic inflammation in rats. 2. To this end we have tested the effects of the B2 receptor antagonists Hoe 140, FR173657 or FR172357 on the pleural inflammatory response triggered by intrapleural (i.pl.) injection of allergen (ovalbumin, 12 microg cavity(-1)) in 14 day-actively sensitized Wistar rats. Analysis of the pleural fluid effluent revealed a sequence of mast cell-dependent inflammatory events, including early protein exudation and neutrophilia and late pleural eosinophil influx. 3. Local treatment with Hoe 140 (0.1 and 1 microg cavity(-1)), FR173657 (1 and 10 microg cavity(-1)) or FR172357 (1 and 10 microg cavity(-1)) inhibited dose-dependently allergen-induced mast cell activation with impairment of pleural plasma leakage, neutrophil accumulation and late eosinophil influx. 4. Moreover, the B2 receptor antagonists also dose-dependently inhibited the allergic like inflammatory pleurisy triggered by bradykinin (50 microg cavity(-1)), which is characterized by acute mast cell degranulation, protein leakage and pleural eosinophil infiltration. 5. Taken together, our findings provide substantial evidence to suggest that bradykinin acting on its B2 receptors play a critical role in mediating allergic mast cell-dependent inflammation in rats, and suggest that B2 receptor antagonists may be useful therapeutically to control allergic dysfunction.
Figures
References
-
- ABE K., WATANABE N., KUMAGAI N., MOURI T., SEKI T., YOSHINAGA K. Circulating plasma kinin in patients with bronchial asthma. Experientia. 1967;23:626–627. - PubMed
-
- ABRAHAM W.M., BURCH R.M., FARMER S.G., AHMED A., CORTES A. A bradykinin antagonist modifies allergen-induced mediator release and late bronchial responses in sheep. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991;143:787–796. - PubMed
-
- AKBARY A.M., WIRTH K.J., SCHÖLKENS B.A. Efficacy and tolerability of Icatibant (Hoe 140) in patients with moderately severe chronic bronchial asthma. Immunopharmacol. 1996;33:238–242. - PubMed
-
- AUSTIN C.E., DEAR J.W., NEIGHBOUR H., LUNG V., FOREMAN J.C. The contribution of histamine to action of bradykinin in the human nasal airway. Immunopharmacol. 1996;34:181–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

