Capsaicin-insensitive sensory-efferent meningeal vasodilatation evoked by electrical stimulation of trigeminal nerve fibres in the rat
- PMID: 10385246
- PMCID: PMC1566033
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702561
Capsaicin-insensitive sensory-efferent meningeal vasodilatation evoked by electrical stimulation of trigeminal nerve fibres in the rat
Abstract
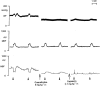
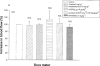
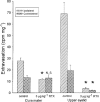
1. Antidromic vasodilatation and plasma extravasation to stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion or its perivascular meningeal fibres was investigated by laser-Doppler flowmetry and 125I-labelled bovin serum albumin in the dura mater and in exteroceptive areas (nasal mucosa, upper eyelid) of anaesthetized rats pretreated with guanethidine and pipecuronium. 2 Trigeminal stimulation at 5 Hz for 20 s elicited unilateral phasic vasodilatation in the dura and lasting response in the nasal mucosa. Resiniferatoxin (1-3 microg kg(-1) i.v.), topical (1%) or systemic capsaicin pretreatment (300 mg kg(-1) s.c. plus 1 mg kg(-1) i.v.) did not inhibit the meningeal responses but abolished or strongly inhibited the nasal responses. Administration of vinpocetine (3 mg kg(-1) i.v.) increased both basal blood flow and the dural vasodilatation to perivascular nerve stimulation. 3. Dural vasodilatation to trigeminal stimulation was not inhibited by the calcitonin gene-related peptide-1 receptor (CGRP-1) antagonist hCGRP8-37 (15 or 50 microg kg(-1) i.v), or the neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist RP 67580 (0.1 mg kg(-1) i.v.) although both antagonists inhibited the nasal response. Neither mucosal nor meningeal responses were inhibited by atropine (5 mg kg(-1) i.v.), hexamethonium (10 mg kg(-1) i.v.) or the vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) antagonist (p-chloro-D-Phe6-Leul7)VIP (20 microg kg(-1) i.v.). 4. Plasma extravasation in the dura and upper eyelid elicited by electrical stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion was almost completely abolished in rats pretreated with resiniferatoxin (3 microg kg(-1) i.v.). 5. It is concluded that in the rat meningeal vasodilatation evoked by stimulation of trigeminal fibres is mediated by capsaicin-insensitive primary afferents, while plasma extravasation in the dura and upper eyelid and the vasodilatation in the nasal mucosa are mediated by capsaicin-sensitive trigeminal fibres.
Figures

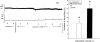
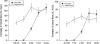



References
-
- CARMODY J., PAWLAK M., MESSLINGER K. Lack of role for substance P in the control of dural arterial flow. Exp. Brain Res. 1996;111:424–428. - PubMed
-
- ESCOTT K.J., BEATTIE D.T., CONNOR H.E., BRAIN S.D. Trigeminal ganglion stimulation increases facial skin blood flow in the rat: a major role for calcitonin gene-related peptide. Brain Res. 1995a;669:93–99. - PubMed
-
- ESCOTT K.J., CONNOR H.E., BRAIN S.D., BEATTIE D.T. The involvement of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P in feline pial artery diameter responses evoked by capsaicin. Neuropeptides. 1995b;29:129–135. - PubMed
-
- FUSCO B.M., FIORE G., GALLO F., MARTELLETTI P., GIACOVAZZO M. Capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons in cluster headache: pathophysiological aspects and therapeutic indication. Headache. 1994;34:132–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

